Microsoft’s Growing Energy Consumption in the AI Era
-
Aug, Thu, 2024
Microsoft’s Growing Energy Consumption in the AI Era
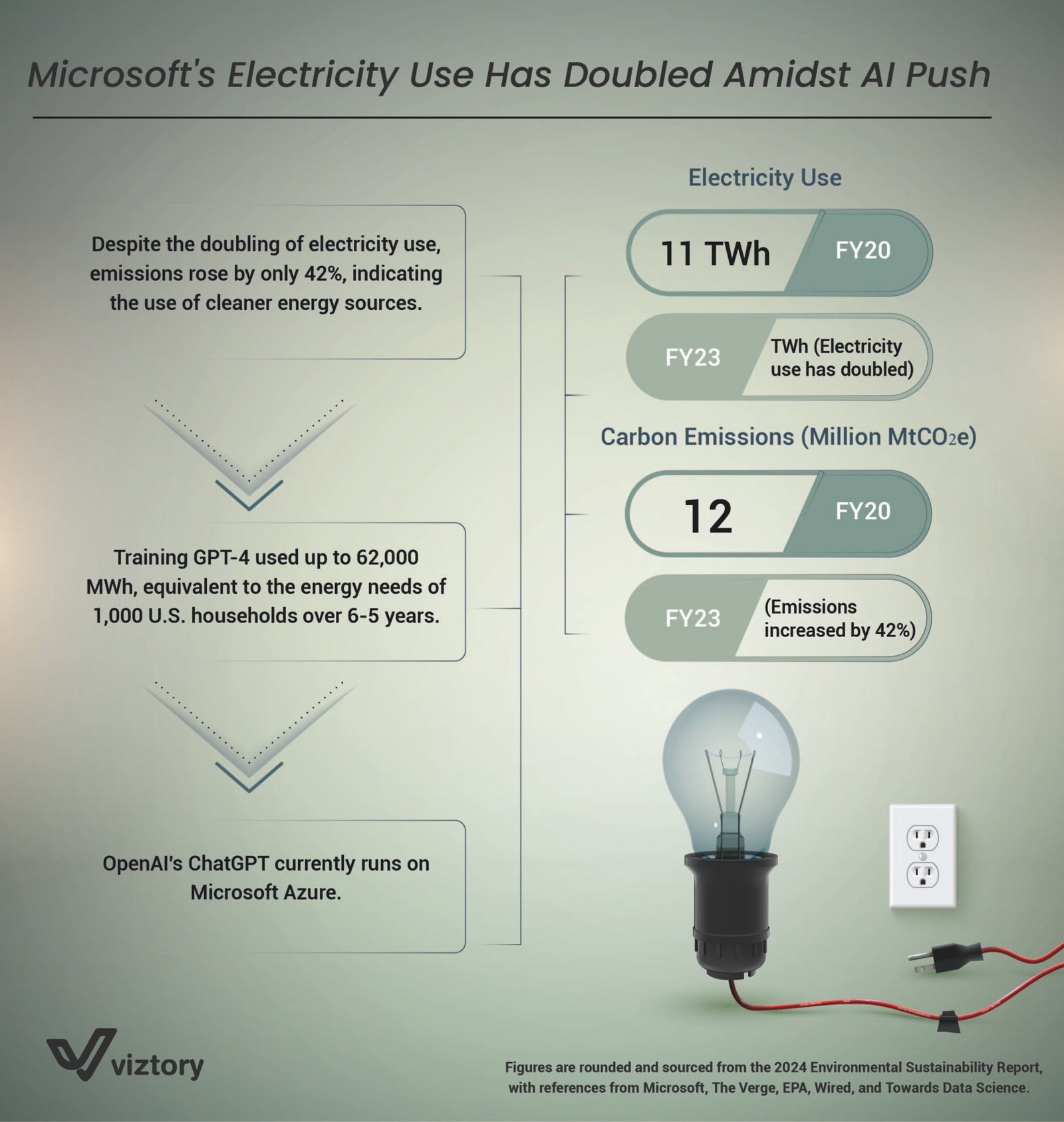
As technology companies push the boundaries of innovation, the demands placed on infrastructure and energy consumption have soared, particularly in the realm of artificial intelligence (AI). The image underscores a striking shift in Microsoft’s energy consumption between fiscal years 2020 (FY20) and 2023 (FY23), revealing that electricity use has doubled as the company has accelerated its AI initiatives. However, despite this substantial increase in energy usage, carbon emissions rose by only 42%, suggesting the company is incorporating more sustainable and cleaner energy sources into its operations.
The Rise of AI and Energy Demand
Artificial intelligence, particularly the development and deployment of advanced models like GPT-4, has contributed significantly to the surge in energy consumption. Training large language models, such as GPT-4, is highly energy-intensive. The infographic points out that training GPT-4 alone required up to 62,000 megawatt-hours (MWh) of electricity — an amount equivalent to powering approximately 1,000 U.S. households over a period of 6-5 years. AI models like GPT-4, developed by OpenAI, run on Microsoft’s Azure cloud infrastructure, placing further strain on energy resources.
The dramatic increase in energy consumption reflects the growing demand for cloud computing, data processing, and AI capabilities. Microsoft’s investment in AI, cloud services, and large-scale data centers drives this consumption, highlighting the energy costs associated with maintaining cutting-edge technological advancements.
Cleaner Energy, Reduced Carbon Footprint
Despite this rise in electricity usage, Microsoft has managed to limit its carbon emissions, increasing by only 42% instead of doubling alongside electricity use. This discrepancy points to the growing incorporation of cleaner energy sources in Microsoft’s operations, likely through renewable energy investments, energy-efficient data centers, and improved sustainability practices. For a company of Microsoft’s scale, balancing technological expansion with environmental responsibility is crucial. In a world grappling with the realities of climate change, this effort signals that large corporations can strive for growth while managing their environmental footprint.
Sustainability in the Tech Industry
This trend reflects a broader shift within the tech industry toward sustainability. Many companies, including Microsoft, have committed to ambitious climate goals, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and utilize renewable energy. The pressures from environmental advocacy groups, regulatory bodies, and the growing awareness among consumers about climate issues are leading tech giants to take proactive measures in sustainable development.
Microsoft has set specific targets to become carbon negative by 2030, meaning it will remove more carbon from the atmosphere than it emits. This shift toward cleaner energy use aligns with its long-term vision of reducing its impact on the environment while still pursuing technological advancements. In the context of AI, this balancing act is particularly difficult because the computational power required to develop and maintain AI systems is enormous. Nevertheless, as the company explores more efficient algorithms, cooling technologies for data centers, and partnerships with green energy providers, it is working to make its AI-driven future more sustainable.
Technology’s Dual-Edged Impact on Energy Consumption
The growth of AI, data centers, and cloud computing has brought unprecedented benefits to industries, driving innovation, economic growth, and new capabilities in fields ranging from healthcare to finance. However, this comes at an environmental cost. The demand for data storage, processing power, and continuous internet connectivity has led to significant increases in energy usage by tech firms worldwide.
The AI industry’s expansion, particularly in training large models and deploying them at scale, has raised concerns about its long-term sustainability. If energy demands continue to rise at the current pace, companies may need to innovate more aggressively in the areas of energy efficiency, waste reduction, and sustainable data center management. The tech industry is increasingly looking toward green computing solutions, such as advanced cooling systems, low-power processors, and even artificial intelligence to optimize energy consumption.
Conclusion
Microsoft’s experience illustrates the complex relationship between technological advancement and energy consumption. The doubling of electricity usage amid the company’s AI push highlights the growing energy demands of digital transformation. However, the smaller rise in emissions signals an effort to harness cleaner energy sources and prioritize sustainability. As AI, cloud computing, and big data continue to expand, companies will face increasing pressure to manage their environmental impact. Microsoft’s approach serves as an example of how the tech industry can work toward a future that is both technologically advanced and environmentally responsible. Balancing these two priorities will be key to ensuring that the benefits of innovation do not come at the expense of the planet’s health.