Trends in Cardiovascular Diseases and Cancer Mortality: A Comparative Healthcare Analysis (1950-2022)
-
Sep, Thu, 2024
Trends in Cardiovascular Diseases and Cancer Mortality: A Comparative Healthcare Analysis (1950-2022)
The global health landscape has undergone significant changes over the last several decades, particularly in relation to non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cardiovascular diseases and cancer. These diseases, once regarded as major public health crises, have seen a notable evolution in mortality trends, largely due to advancements in healthcare, medical technology, and public health interventions.
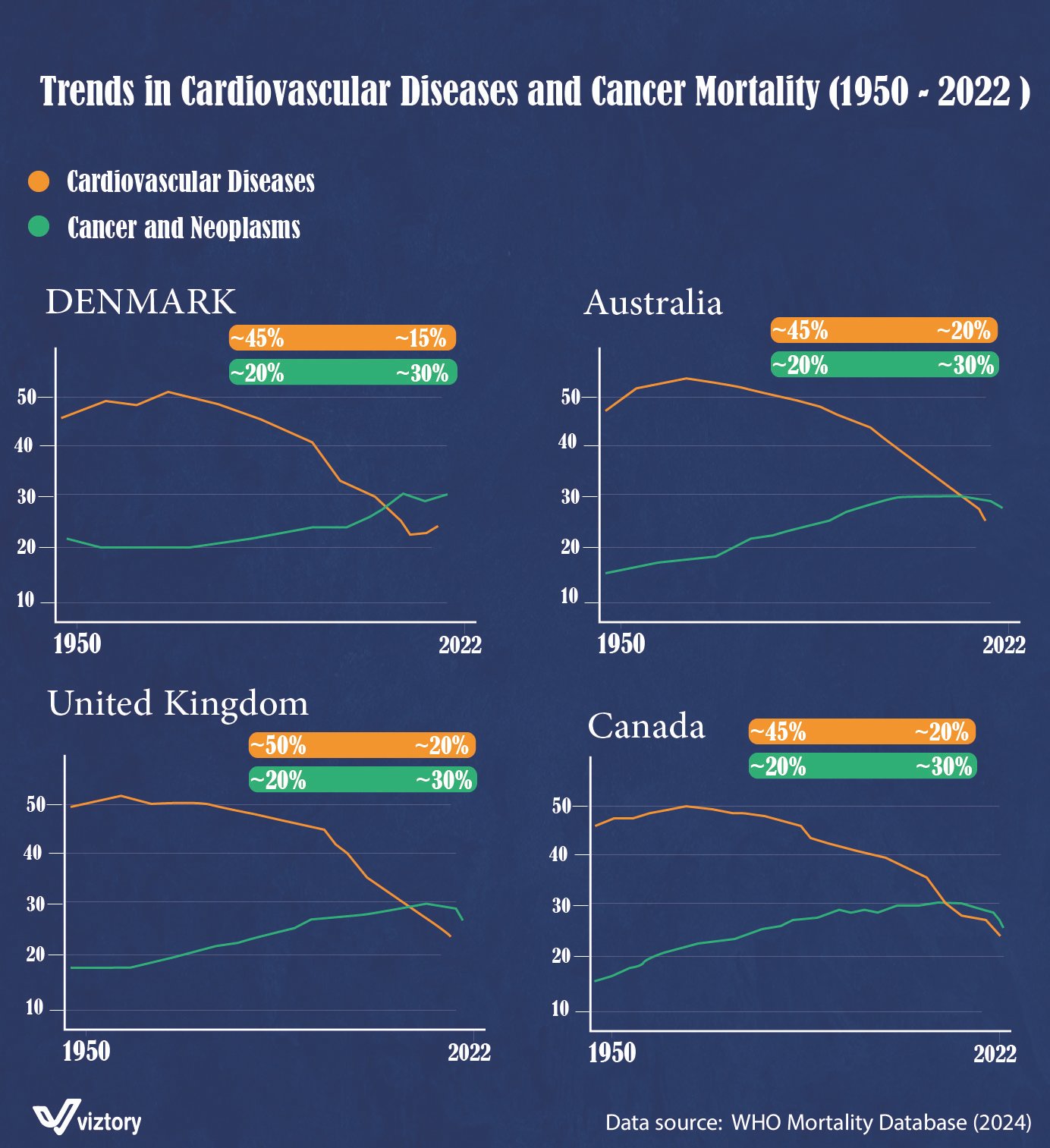
The infographic presents an in-depth analysis of cardiovascular diseases and cancer mortality rates from 1950 to 2022 in four countries: Denmark, Australia, the United Kingdom, and Canada. The visual comparison highlights the remarkable strides made in reducing mortality from cardiovascular diseases while shedding light on the rising concerns regarding cancer mortality.
1. Cardiovascular Disease Mortality: A Steady Decline
Across all four countries, cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and strokes, have historically been the leading cause of death. However, from the 1950s onwards, these nations have seen a significant decline in mortality rates from these diseases:
- Denmark: Cardiovascular mortality has decreased by ~45% since the 1950s and now stands at approximately 15% of the total mortality rate.
- Australia: Similarly, Australia saw a ~45% reduction in cardiovascular deaths, with current levels reduced to ~20%.
- United Kingdom: Mortality rates from cardiovascular diseases decreased even more, by approximately 50%, down to ~20%.
- Canada: Cardiovascular mortality in Canada has fallen by ~45% since the 1950s, with the current figure hovering at ~20%.
This decline can be attributed to several healthcare improvements, including:
- Enhanced medical interventions: Breakthroughs such as angioplasty, stents, and advanced cardiac surgery have significantly improved outcomes for patients with cardiovascular conditions.
- Public health policies: Anti-smoking campaigns, dietary guidelines, and programs encouraging physical activity have also contributed to reducing risk factors for heart disease.
- Preventive care: Early detection through regular health screenings has helped to identify and mitigate risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
2. Cancer Mortality: A Complex Trend
The trend in cancer mortality presents a different picture. While the mortality rate for cardiovascular diseases has dramatically decreased, cancer-related deaths have followed a more complex trajectory:
- Denmark: Cancer mortality rates initially decreased by ~20%, but recent data shows a resurgence to ~30%.
- Australia: Cancer deaths have decreased by ~20%, with current figures showing a rise to ~30%.
- United Kingdom: Cancer mortality decreased by ~20% but currently stands at around ~30%.
- Canada: Similarly, cancer mortality in Canada dropped by ~20% before rising again to ~30%.
While cancer treatments have improved, the gradual increase in cancer mortality could be linked to:
- Aging populations: As people live longer due to better healthcare for other conditions, they are more likely to develop cancer later in life.
- Environmental factors: Increased exposure to carcinogens, lifestyle factors, and changes in dietary habits may contribute to the rising cancer incidence.
- Advances in diagnosis: Earlier and more precise cancer diagnoses may account for the rise in recorded cancer mortality, reflecting both improvements in healthcare and the growing prevalence of certain cancers.
3. The Role of Healthcare Systems
The trends illustrated in the graph underscore the critical role healthcare systems play in combating non-communicable diseases. Countries with robust healthcare infrastructures, such as Denmark, Australia, the United Kingdom, and Canada, have been able to effectively reduce cardiovascular mortality through a combination of preventive care, public health initiatives, and advanced medical technologies.
Cancer mortality, however, presents new challenges for these healthcare systems. With the rise in cancer incidence, healthcare providers and governments must continue to invest in:
- Cancer research and innovation: Ongoing research into targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and precision medicine is crucial for developing effective treatments for cancer.
- Public health education: Raising awareness about cancer prevention through screenings, vaccinations (such as the HPV vaccine), and lifestyle changes is essential for reducing cancer incidence.
- Healthcare accessibility: Ensuring that cancer care is accessible to all segments of the population, particularly marginalized groups, will be vital for improving cancer outcomes and reducing mortality.
Conclusion
The infographic provides a compelling snapshot of the progress made in combating cardiovascular diseases, while also highlighting the persistent challenges posed by cancer mortality. The data from Denmark, Australia, the United Kingdom, and Canada reveal how effective public health interventions and healthcare advancements have reshaped the landscape of non-communicable diseases. Going forward, healthcare systems must continue to adapt and innovate to address the rising cancer mortality rates, ensuring that future generations can enjoy longer and healthier lives.
The trends presented are a testament to the power of healthcare systems, technological advancements, and proactive public health strategies. However, as cancer continues to pose a significant challenge, there remains an urgent need for global cooperation, investment in research, and a commitment to accessible healthcare for all.