U.S. Jobs with the Biggest Projected Declines
-
Oct, Fri, 2024
U.S. Jobs with the Biggest Projected Declines: Financial Implications and Economic Shifts
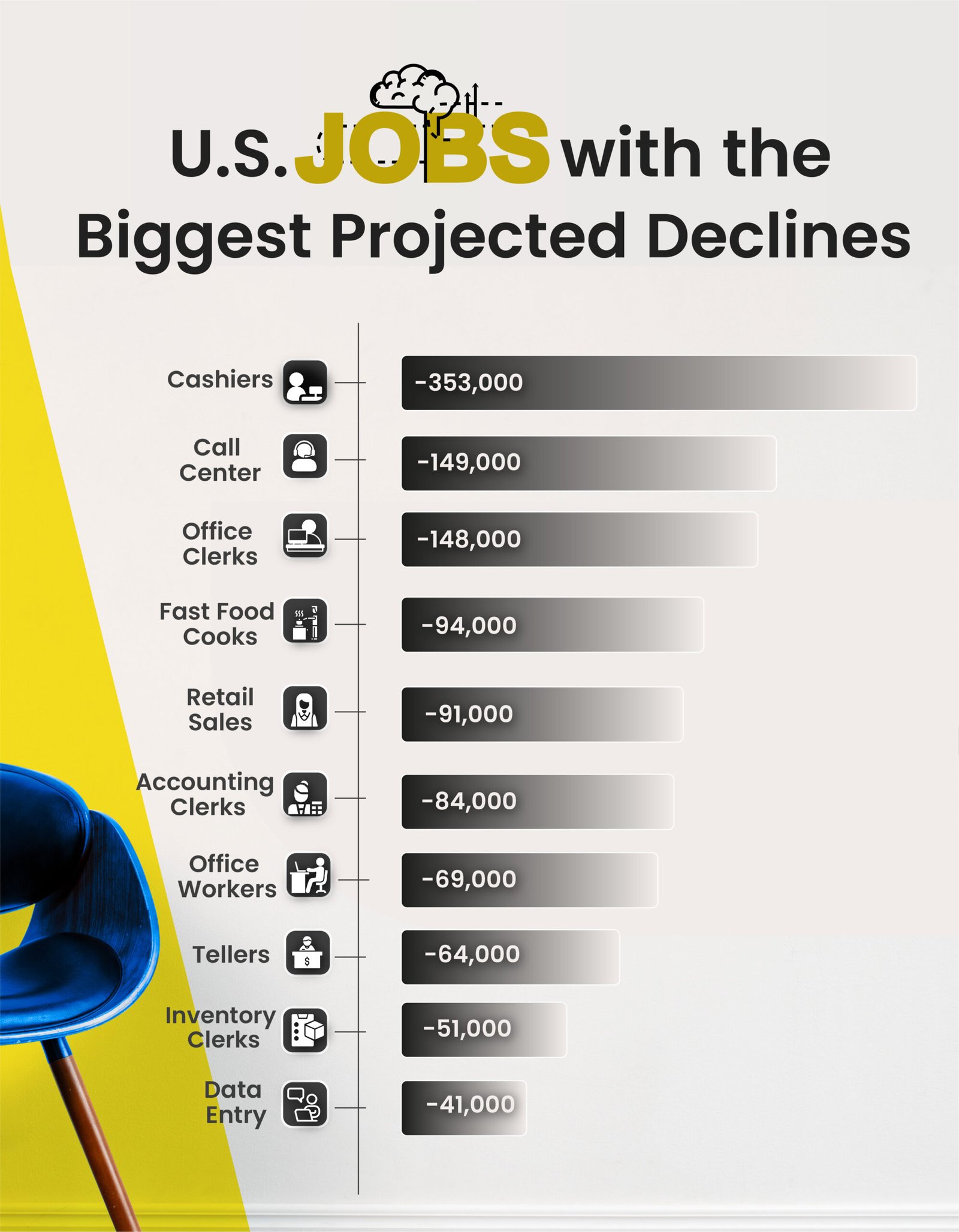
The visualization highlights a projected decline in various U.S. jobs, with significant losses expected in roles such as cashiers, call center agents, and office clerks. These job reductions indicate a broader economic shift driven by automation, digitalization, and changing consumer behaviors. The decline in these positions has substantial financial implications for both individuals and the economy, as well as a ripple effect on industries connected to these roles.
Financial Impact on Individuals and Households
The job categories facing the steepest declines are largely those that typically offer entry-level positions with limited educational requirements. With 353,000 cashier jobs projected to decline, many individuals may find themselves without a primary source of income, affecting household stability and consumer spending. Similarly, reductions in call center and office clerk positions (149,000 and 148,000, respectively) could disproportionately impact those without specialized skills, potentially increasing the demand for social support and unemployment benefits.
Implications for Consumer Spending and Economic Growth
As these jobs disappear, the loss of wages for affected workers could lead to decreased consumer spending, which is a major driver of economic growth. Industries that rely on discretionary spending, such as retail and dining, may feel the impact as individuals cut back on non-essential purchases. Additionally, a decline in fast food cooks and retail sales jobs could result in reduced operational hours and services in these sectors, which could further affect sales and profitability, creating a negative feedback loop that affects the broader economy.
The Role of Automation and Technology in Job Displacement
Automation and technological advancements are significant contributors to the decline in these roles. For example, self-checkout systems and online customer service platforms are replacing cashiers and call center agents, respectively. This shift not only reduces labor costs for businesses but also impacts wage growth and job security. Similarly, the rise of digital tools for data processing has lessened the need for data entry and accounting clerks, leading to an anticipated reduction of 41,000 and 84,000 jobs, respectively.
Economic Shift Toward Higher-Skilled Positions
The decline in these jobs reflects an ongoing transition toward an economy that favors higher-skilled and technology-focused positions. As traditional roles diminish, there is an increasing demand for workers with skills in IT, data analysis, and other specialized fields. Programs that offer reskilling and upskilling opportunities can play a crucial role in helping displaced workers transition into emerging fields, ensuring that they remain economically productive and reducing reliance on financial assistance programs.
Conclusion
The projected decline in these job categories underscores the need for strategic responses to mitigate the financial impact on individuals and the economy. By investing in education and workforce development programs, the U.S. can help affected workers acquire new skills, enabling them to transition into roles that are less susceptible to automation. Proactively addressing these shifts will not only support economic resilience but also promote a more adaptable workforce capable of thriving in an evolving job market.