Top Healthiest Countries in 2024
-
Oct, Fri, 2024
Top Healthiest Countries in 2024: A Healthcare Success Story
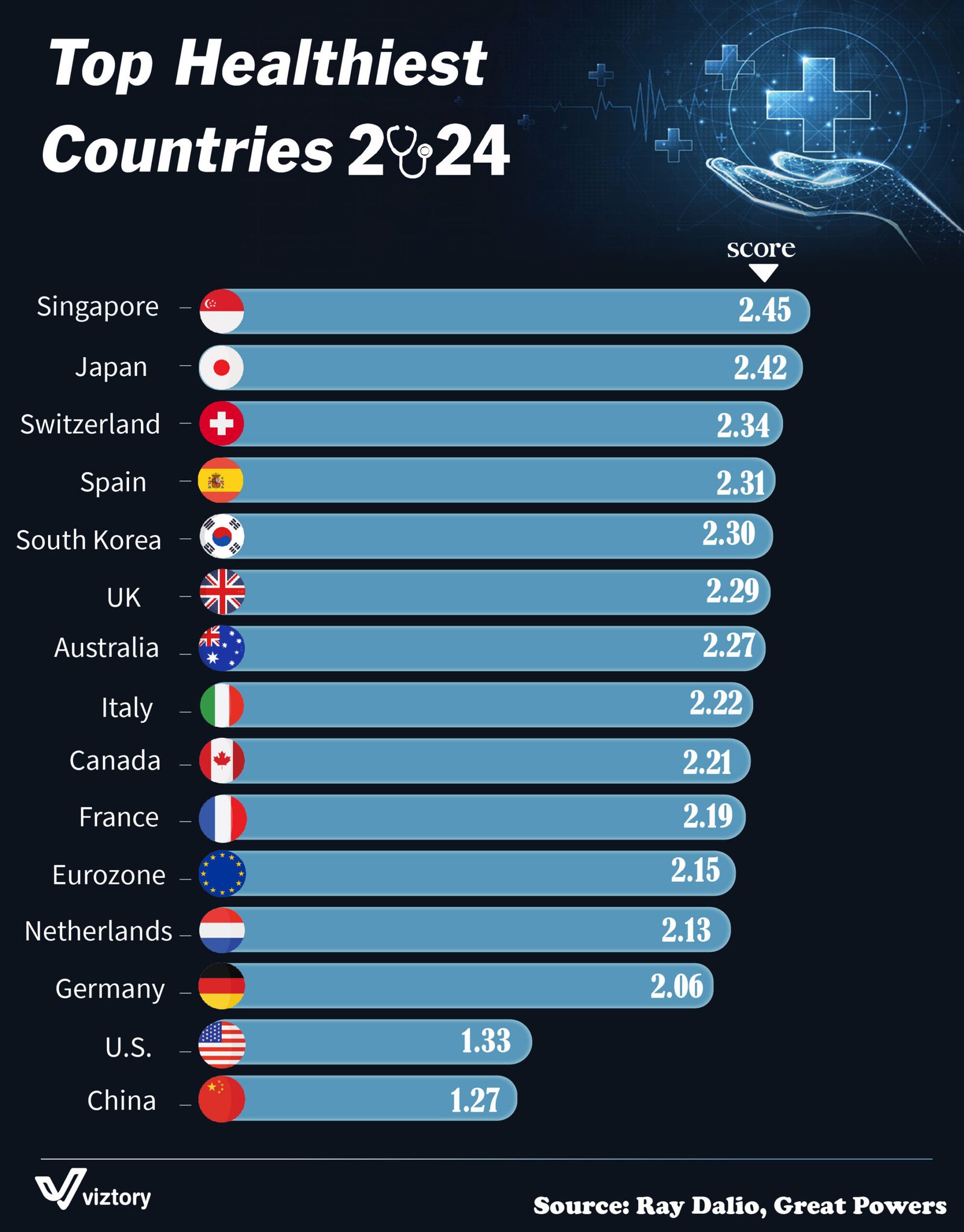
The visual ranking of the healthiest countries in 2024 reveals a compelling picture of global health achievements. Singapore, Japan, and Switzerland top the list, while the United States and China find themselves significantly lower. These rankings are based on a combination of factors such as healthcare access, life expectancy, and public health policies, reflecting how each nation’s healthcare system contributes to overall well-being.
What Makes a Country Healthy?
To be ranked among the healthiest countries, several factors come into play. The score given to each country is a reflection of metrics like life expectancy, healthcare quality, disease prevention, and overall public health infrastructure. Countries like Singapore (2.45) and Japan (2.42), which lead the list, have made significant investments in healthcare, both in terms of infrastructure and policy, fostering a culture of preventive care, health education, and efficient healthcare delivery systems.
Singapore and Japan: A Model of Healthcare Excellence
Singapore has consistently been at the top of global health rankings, thanks to its efficient and innovative healthcare system. The country’s approach to healthcare emphasizes preventive care and technology-driven solutions, making healthcare affordable and accessible to all citizens. Singapore’s success can be attributed to its strict regulations on food safety, environmental health policies, and a healthcare system that balances public and private healthcare services.
Japan, which follows closely with a score of 2.42, is renowned for having one of the highest life expectancies in the world. The country’s success is largely due to its universal healthcare system, which ensures that every citizen has access to medical care, including the elderly. Japan’s healthcare focus on aging populations has allowed the country to address chronic diseases and geriatric care more effectively than many of its counterparts.
Switzerland and Spain: Public Health and Quality of Life
Switzerland’s healthcare system, which earned it a score of 2.34, is widely regarded for its high-quality services and comprehensive coverage. The Swiss healthcare system is a mix of public, subsidized private, and private healthcare plans, ensuring extensive coverage for its citizens. Switzerland’s health-conscious lifestyle, combined with efficient healthcare management, plays a significant role in keeping the population healthy.
Spain, with a score of 2.31, boasts a public healthcare system that is not only accessible but highly effective. Spain’s focus on healthy living, nutrition, and preventive care has contributed to its high health ranking. The country’s Mediterranean diet, coupled with an emphasis on physical activity and primary healthcare, has helped maintain low rates of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
The Role of Public Health in the Healthiest Countries
Countries like South Korea, the UK, and Australia, all of which rank highly on the list, have one thing in common: strong public health systems. These countries prioritize preventive care, have excellent vaccination programs, and work to minimize health disparities across different population groups. For example, the UK’s National Health Service (NHS) provides free medical care at the point of delivery, ensuring that everyone has access to healthcare regardless of income.
Australia’s public health system, which is a blend of public and private care, has contributed to the country’s score of 2.27. Like many top-ranking countries, Australia places a heavy emphasis on preventive care, mental health services, and chronic disease management, all of which contribute to its standing as one of the world’s healthiest nations.
The U.S. and China: Lagging Behind Despite Economic Power
It is notable that the United States, despite being one of the wealthiest countries in the world, has a score of just 1.33, placing it near the bottom of this list. The U.S. healthcare system is often criticized for its high costs, inequality in access, and significant gaps in coverage, all of which contribute to poorer health outcomes compared to its global peers. Issues such as obesity, chronic disease, and limited access to affordable healthcare in many regions have caused the U.S. to lag behind countries with more equitable and accessible healthcare systems.
China, with a score of 1.27, faces similar challenges despite being a global economic power. Rapid urbanization, environmental pollution, and an aging population have strained China’s healthcare system. While China has made considerable strides in expanding healthcare access, particularly in rural areas, its healthcare system still struggles with issues like overcrowding, quality disparities, and rising healthcare costs.
Healthcare and Economic Growth
There is a clear correlation between a country’s healthcare system and its overall economic prosperity. Healthier populations are more productive, which in turn stimulates economic growth. Countries like Switzerland and Singapore, which have strong economies, invest significantly in healthcare, ensuring that their citizens remain healthy and active.
Conversely, countries with lower health rankings, such as the U.S. and China, often face higher healthcare costs, which can impede economic growth. Rising healthcare expenses due to preventable diseases and chronic conditions place a significant financial burden on both individuals and governments.
Conclusion: Investing in Health is Investing in the Future
The rankings of the healthiest countries in 2024 highlight the importance of robust healthcare systems, public health policies, and lifestyle factors in promoting overall well-being. Countries that invest in preventive care, universal access, and chronic disease management not only achieve better health outcomes but also create healthier, more prosperous societies.
As countries like Singapore and Japan demonstrate, a strong healthcare system is key to longevity and quality of life. On the other hand, nations with less efficient healthcare models, such as the United States and China, must take bold steps to address the gaps in their healthcare systems if they wish to improve their population’s health and secure long-term economic success.