Global Child Deaths Due to Malnutrition: Low Birth Weight Tops the List in 2021
-
Sep, Sun, 2024
Global Child Deaths Due to Malnutrition: Low Birth Weight Tops the List in 2021
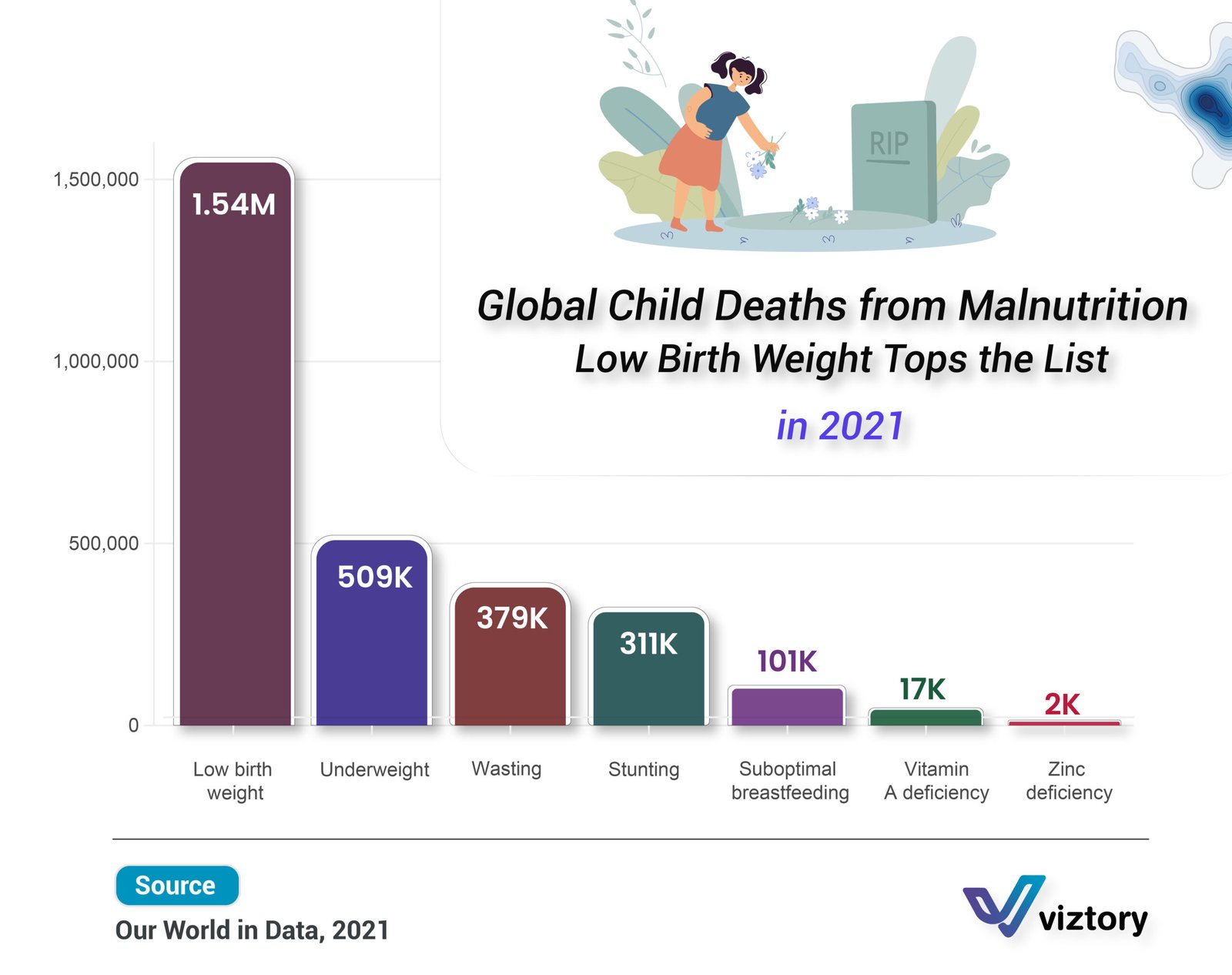
The attached infographic highlights the devastating impact of malnutrition among children worldwide, with low birth weight emerging as the leading cause of death related to malnutrition in 2021. This issue underscores the importance of improving maternal and newborn healthcare, which is a critical component of efforts to enhance healthcare systems globally.
Key Issues Caused by Malnutrition:
- Low Birth Weight: Ranked first with the highest number of deaths, affecting 1.54 million children. This indicator serves as a critical reminder of the need for better maternal care during pregnancy to improve birth outcomes.
- Underweight: Malnutrition related to underweight conditions accounted for around 509,000 deaths, indicating continued undernutrition in children’s early developmental stages.
- Wasting: Severe acute malnutrition, also known as wasting, led to 379,000 deaths among children.
- Stunting: An abnormal growth pattern resulting from chronic malnutrition caused the deaths of 311,000 children. Stunting is a long-term consequence of inadequate nutrition.
- Suboptimal Breastfeeding: The data shows that 101,000 children died as a result of inadequate nutrition due to insufficient breastfeeding.
- Vitamin A Deficiency: A vital nutrient for children’s growth, the deficiency of Vitamin A contributed to the deaths of 17,000 children.
- Zinc Deficiency: Although less common, the lack of zinc led to the deaths of 2,000 children, a smaller figure compared to other causes but still alarming.
The Role of Healthcare:
From a healthcare perspective, these numbers highlight the urgent need to improve global nutrition programs, particularly in communities that suffer from poverty and lack access to essential healthcare. The critical role that improving nutrition during pregnancy and the postnatal period plays in reducing malnutrition-related mortality cannot be overstated.
There is also a need to focus on raising awareness about the importance of adequate breastfeeding and providing nutritional supplements such as Vitamin A and zinc to mothers and children, as these nutrients are crucial for proper child development.
Conclusion:
The global healthcare community must recognize the importance of addressing child malnutrition as a fundamental health issue. As shown in the 2021 data, low birth weight is the leading cause of child deaths from malnutrition, followed by underweight and wasting. These preventable deaths call for increased investment in maternal healthcare and child nutrition programs, especially in regions where healthcare infrastructure is lacking.
Healthcare systems must prioritize maternal and infant care by improving access to prenatal care, educating mothers on the benefits of breastfeeding, and ensuring that vital nutrients such as Vitamin A and zinc are available. By addressing these challenges, global healthcare can reduce child mortality rates and foster healthier futures for millions of children worldwide.