Global Coal Consumption in 2023 and the Role of Technology in Reducing Dependency
-
Sep, Thu, 2024
Global Coal Consumption in 2023 and the Role of Technology in Reducing Dependency
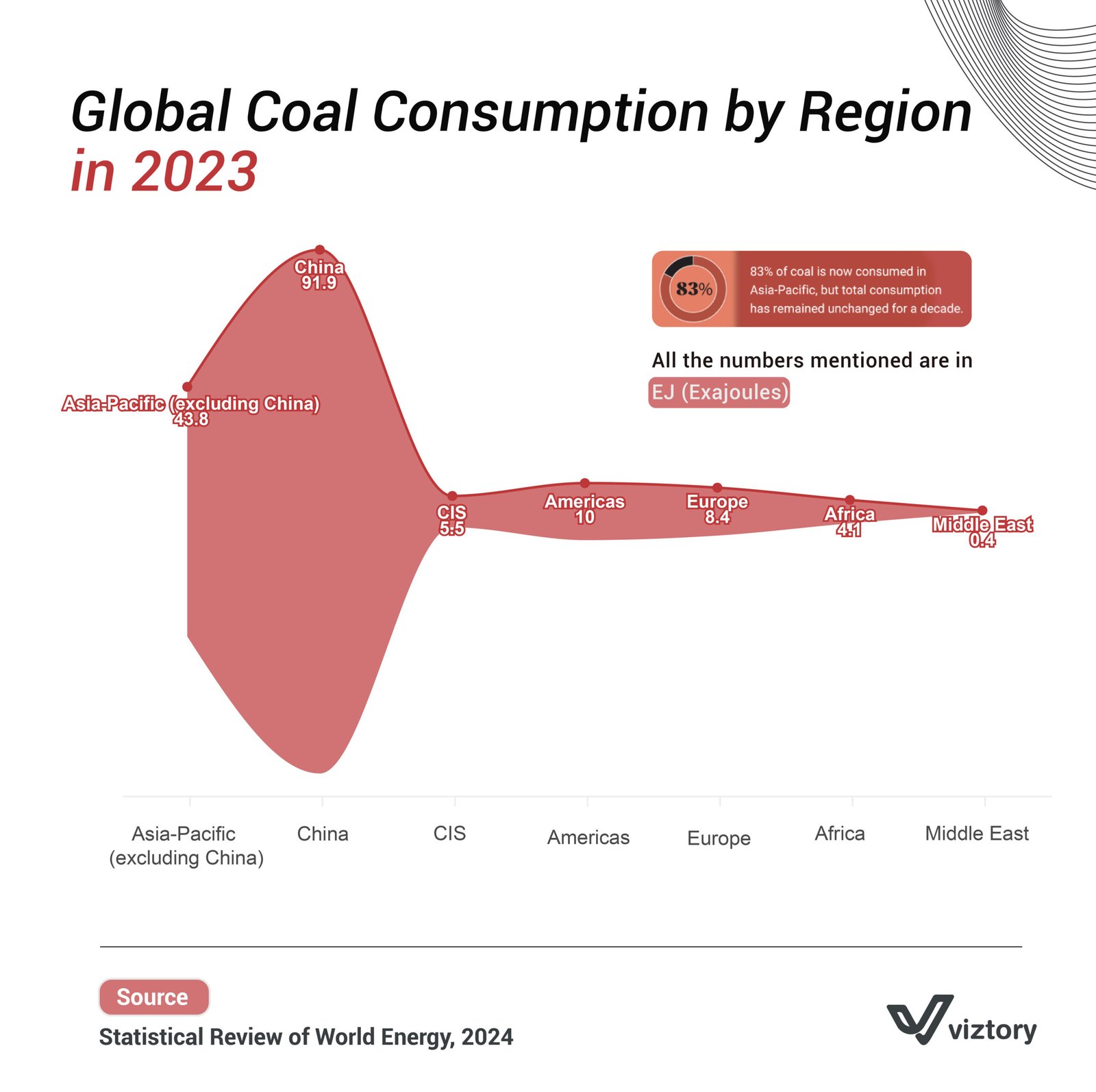
The image showing global coal consumption by region in 2023 reveals critical insights into how the world continues to rely on coal as an energy source, despite growing concerns about climate change and sustainability. China, accounting for 91.9 exajoules (EJ), dominates global coal consumption, while the Asia-Pacific region (excluding China) follows with 43.8 EJ. Together, these regions account for 83% of the world’s coal usage. Although global coal consumption has remained relatively stable for a decade, the energy landscape is on the cusp of major shifts due to technological advancements.
The Role of Coal in the Energy Sector
Coal remains a significant energy source, particularly in industrialized and rapidly developing nations. The sheer scale of consumption in China and the Asia-Pacific reflects the region’s dependence on coal for electricity generation, manufacturing, and heavy industries. However, this reliance comes with major drawbacks. Coal is a leading contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, and environmental degradation. This presents an urgent need for alternative energy sources, and technology plays a pivotal role in accelerating the transition to cleaner forms of energy.
Technology as a Catalyst for Change
While coal consumption continues to play a major role in the global energy mix, technology is paving the way for significant changes. Innovations in renewable energy technology, carbon capture, and energy efficiency can reduce global reliance on coal.
Renewable Energy Technologies: Renewable energy technologies, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, have advanced significantly in recent years. Countries around the world are increasingly investing in these technologies, recognizing their potential to replace coal as a major source of energy. Solar and wind power have become more cost-effective and scalable, helping to reduce the global reliance on coal for electricity generation. As the cost of renewable energy continues to fall, it is expected that regions heavily dependent on coal, like Asia-Pacific, will begin transitioning toward cleaner energy sources.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): For countries that are unlikely to abandon coal immediately, carbon capture and storage technology offers a potential solution to mitigate environmental damage. CCS technology captures carbon dioxide emissions from coal plants before they enter the atmosphere and stores them underground. Although this technology is still being developed and has yet to be widely adopted, it represents a critical opportunity to reduce emissions from coal-burning power plants.
Energy Efficiency and Smart Grids: Advances in energy efficiency and smart grid technologies also play a role in reducing coal consumption. Smart grids allow for better management of electricity demand and distribution, making it easier to integrate renewable energy into national grids and reduce reliance on coal. Energy efficiency technologies, such as LED lighting, energy-efficient appliances, and better insulation in buildings, reduce overall energy consumption, decreasing the need for coal-generated electricity.
Challenges to Reducing Coal Dependency
While technology offers numerous solutions for reducing coal consumption, several challenges remain. First, the infrastructure for coal energy is deeply entrenched in many countries, especially in China and the Asia-Pacific region. Transitioning to renewables requires significant investments in infrastructure, grid upgrades, and training for energy workers.
Furthermore, the political and economic importance of coal in certain regions cannot be understated. In many developing countries, coal is not only an energy source but also a source of employment and economic growth. Without careful management, the shift away from coal could lead to economic disruptions and job losses.
Finally, despite advancements in renewable energy, coal remains a more reliable and constant energy source compared to intermittent sources like solar and wind. Until battery storage technology advances enough to provide consistent power during times when renewable sources are not producing, coal may remain a key part of the energy landscape.
The Path Forward: Balancing Innovation and Practicality
The image depicting coal consumption by region in 2023 highlights the ongoing challenge of reducing global coal dependency. However, technology holds the key to reshaping the global energy mix. Governments and industries worldwide must prioritize investments in renewable energy technologies, develop carbon capture solutions, and improve energy efficiency.
Ultimately, the transition away from coal will require a combination of technological innovation, political will, and international cooperation. The next decade will likely see significant changes in how energy is produced and consumed globally, with technology driving the shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions.
Conclusion
As the image illustrates, coal remains a significant part of the global energy landscape, particularly in Asia-Pacific. However, advances in renewable energy, carbon capture, and smart grid technologies are setting the stage for a major transition. By leveraging these technologies, the world can reduce its reliance on coal, protect the environment, and ensure a healthier, more sustainable future.