Global Inflation: Signs of Stabilization Expected in 2024
-
Aug, Fri, 2024
Global Inflation: Signs of Stabilization Expected in 2024
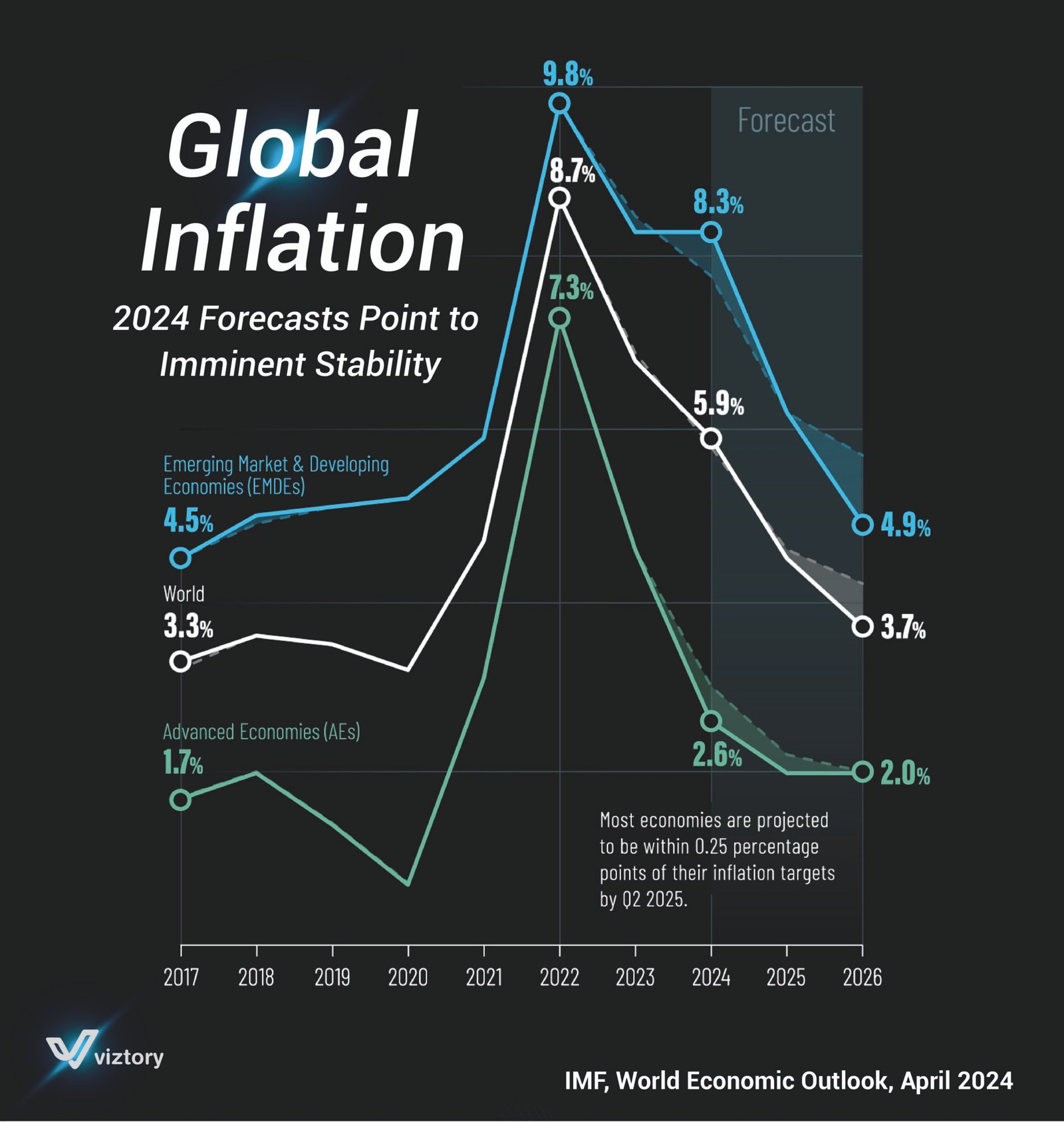
The image highlights global inflation forecasts from 2017 to 2026, with a focus on 2024, which is expected to witness significant stabilization. These projections are based on the “IMF World Economic Outlook” report released in April 2024.
Inflation: Understanding the Economic Fundamentals
Inflation refers to the general rise in prices of goods and services, which decreases the purchasing power of money. As inflation rises, individuals and businesses need to spend more money to purchase the same amount of goods or services. Inflation is a major challenge for global economies as it affects living standards, investments, and overall economic growth.
Analyzing Historical Inflation Trends (2017-2023)
Over the past few years, the world has experienced sharp fluctuations in inflation rates. In 2020, the global COVID-19 pandemic disrupted supply chains and increased demand for certain essential goods, leading to unprecedented spikes in inflation.
Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDEs) were more affected, with inflation rates in these economies rising from 4.5% in 2017 to a peak of 9.8% in 2022. This significant increase was driven by a combination of factors, including currency fluctuations, weak financial institutions, and heavy reliance on imports.
On the other hand, Advanced Economies (AEs), with more stable economic structures, saw inflation rise from 1.7% in 2017 to 7.3% in 2022. Although this increase was substantial, it was less severe compared to emerging economies.
Future Projections (2024-2026)
According to the forecasts, inflation is expected to decrease significantly starting in 2024, with Advanced Economies seeing a decline to 2.6% by 2024 and 2.0% by 2026, indicating a return to targeted inflation ranges.
For Emerging Market Economies, inflation is expected to decrease to 4.9% in 2024 and 4.5% in 2026. However, these rates will remain higher compared to advanced economies, reflecting ongoing challenges such as geopolitical factors and heavy dependence on raw materials and commodities.
Economic Impacts of Inflation
Controlling inflation is one of the primary economic goals of governments and central banks. Prolonged high inflation can erode individuals’ savings, increase borrowing costs, and slow down economic growth. Therefore, governments must adopt balanced monetary and fiscal policies to ensure economic stability.
The Role of Monetary Policies in Managing Inflation
Monetary policies play a crucial role in managing inflation. For instance, central banks can raise interest rates to curb inflation by reducing consumer demand. In advanced economies like the United States and the Eurozone, these tools have been effective in lowering inflation rates after periods of increase.
In emerging economies, using monetary policies is more complex due to structural challenges. Therefore, these countries need to focus on enhancing economic stability and increasing economic diversification to mitigate the impact of inflation.
Conclusion
Economic forecasts suggest that the world will witness stabilization in inflation rates starting in 2024. However, there are still many challenges facing economies, especially emerging ones, in achieving this stability. Controlling inflation will remain a fundamental goal to ensure sustainable economic growth and improve living standards globally.