Global Obesity Trends and Healthcare Challenges
-
Oct, Fri, 2024
Global Obesity Trends and Healthcare Challenges
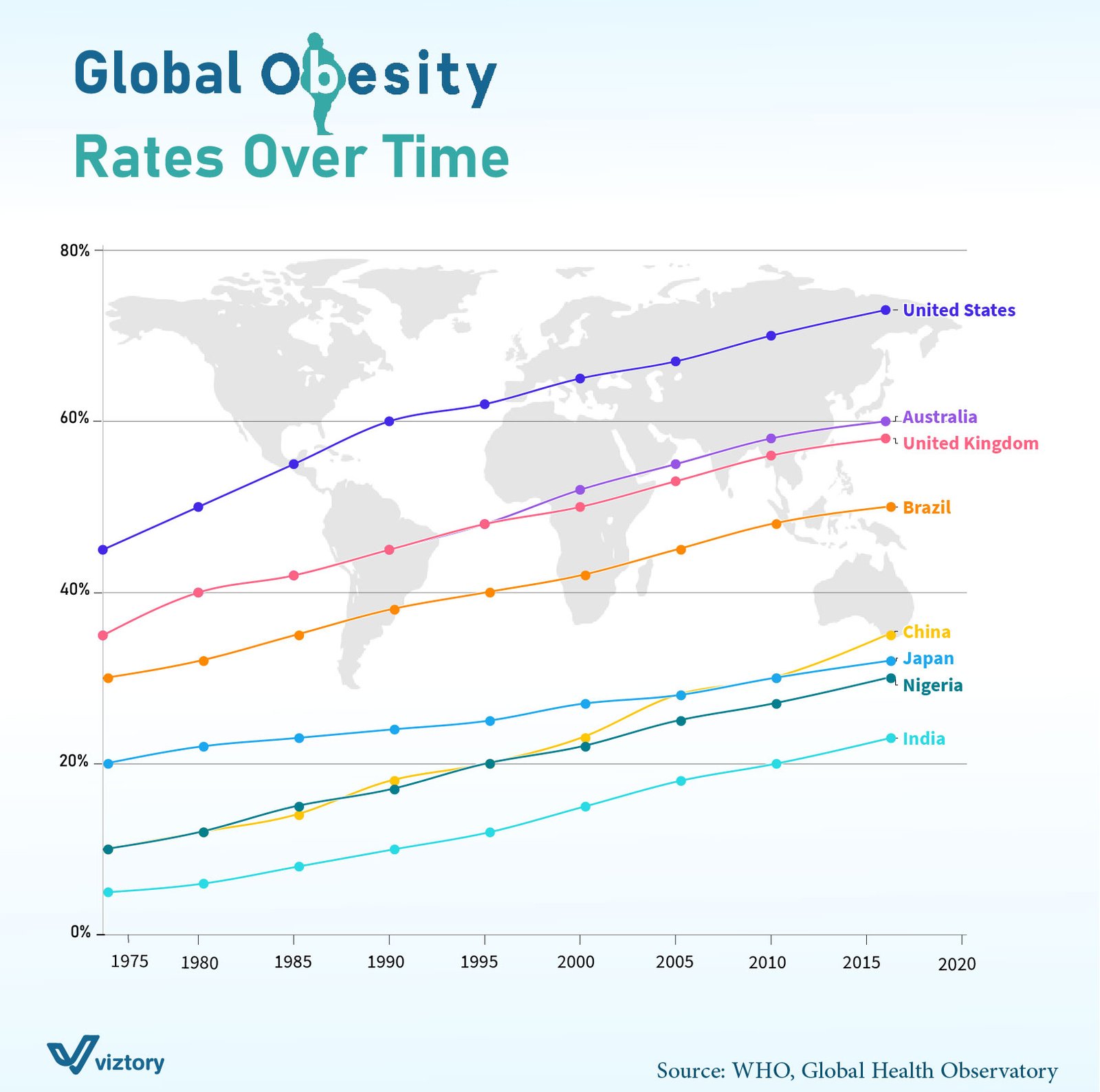
The growing global obesity epidemic is highlighted in the visual representation, showcasing the increase in obesity rates across multiple countries over time. Nations like the United States, Australia, and the United Kingdom are facing alarming spikes in obesity, while emerging economies like China, Brazil, and India also see rising trends, albeit at varying rates. These shifts in population health carry significant implications for healthcare systems worldwide, pushing them to adapt to a rapidly evolving public health landscape.
Obesity as a Global Health Crisis
Obesity is not just a lifestyle issue but a multifaceted public health challenge. As highlighted in the graph, the rise in obesity rates in developed countries like the United States, where rates have surged beyond 60%, signifies a trend that affects all aspects of healthcare, from chronic disease management to healthcare costs. The global increase in obesity is associated with a rise in non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular conditions, all of which put immense pressure on healthcare infrastructure.
Chronic Disease Burden and Long-term Care
The trajectory of obesity-related health issues underscores the urgent need for healthcare systems to shift focus from acute care to managing long-term chronic diseases. Obesity is a significant risk factor for conditions such as Type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Countries like Brazil and China, where obesity rates are steadily climbing, must prepare for an increased burden of NCDs. For instance, Brazil’s healthcare system will need to allocate more resources toward specialized care for obesity-induced complications, requiring both public health interventions and individual-level medical management.
Regional Variations in Obesity and Healthcare Response
While developed countries like Australia and the United Kingdom have some of the highest obesity rates, developing nations such as India and Nigeria show slower but steadily increasing trends. This calls for a nuanced healthcare response that takes into account regional variations in healthcare infrastructure, socioeconomic factors, and population needs. India’s healthcare system, for instance, is still grappling with infectious diseases while also facing a burgeoning obesity epidemic. Balancing the dual burden of infectious and non-communicable diseases will require comprehensive public health strategies.
Healthcare Costs and Resource Allocation
As obesity rates rise, so do the associated healthcare costs. Managing obesity and its related complications demands a significant allocation of resources toward healthcare services. In countries like the United States, where obesity rates have peaked over 60%, healthcare spending on obesity-related conditions is expected to escalate. For developing countries, the financial burden of treating obesity-related NCDs might outpace the available healthcare funding, leading to strained resources and potential gaps in care for vulnerable populations.
Prevention: A Key Focus for Future Healthcare
The rising global obesity trend calls for a rethinking of public health approaches. Preventive measures, including promoting healthier lifestyles through diet and physical activity, are crucial in addressing this epidemic. Countries must invest in public health campaigns aimed at curbing obesity from a young age, along with policies that encourage physical activity and improve access to nutritious foods. These preventive strategies not only mitigate the rise of obesity but also reduce the long-term burden on healthcare systems.
Global Collaboration for Tackling Obesity
Tackling the obesity epidemic requires a global response, with countries sharing knowledge, research, and strategies to prevent and manage obesity. International organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) play a vital role in providing guidance and policy recommendations. Nations must adopt both population-wide interventions and targeted programs for high-risk groups to effectively combat obesity.
Conclusion
The global rise in obesity rates, as illustrated in the visualization, is a stark reminder of the evolving challenges faced by healthcare systems worldwide. As the prevalence of obesity increases, so does the need for adaptive healthcare responses that prioritize chronic disease management, preventive healthcare, and resource allocation. Countries across the globe must act swiftly to address this public health crisis, implementing robust healthcare policies and strategies to mitigate the long-term impacts of obesity on population health and healthcare infrastructure.