Investing Strategies Across Generations
-
Oct, Tue, 2024
Investing Strategies Across Generations: Money Management Trends in 2024
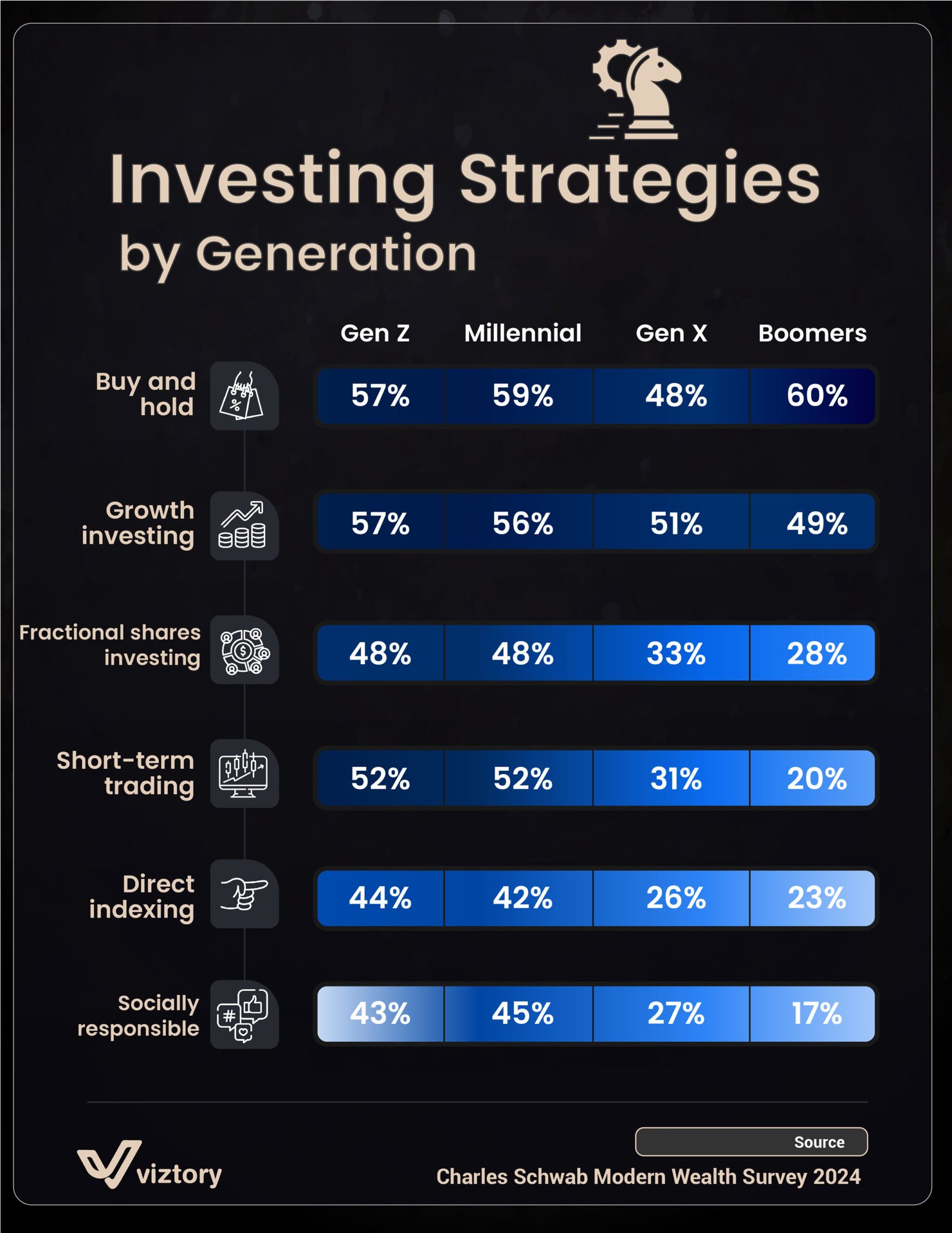
The 2024 Charles Schwab Modern Wealth Survey reveals how different generations approach investing, highlighting trends in financial strategies that reflect varying priorities and risk appetites. From buy-and-hold strategies to socially responsible investing, each generation exhibits distinct preferences that shape their financial landscape. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone seeking to optimize their investment approach in a rapidly evolving market.
Buy and Hold: A Preferred Strategy for Stability
The buy-and-hold strategy remains popular across all generations, with Baby Boomers leading at 60%, followed closely by Millennials and Gen Z at 59% and 57%, respectively. This approach, characterized by a long-term investment horizon, reflects a preference for stability and steady growth. In uncertain economic times, buy-and-hold provides a sense of security, allowing investors to ride out market fluctuations and capitalize on compound interest. For those prioritizing wealth preservation, this strategy aligns with a conservative approach to money management.
Growth Investing and the Pursuit of High Returns
Growth investing appeals to younger generations, particularly Gen Z and Millennials, with 57% and 56% participation rates, respectively. This strategy focuses on investing in companies expected to grow at an above-average rate, offering potentially high returns. However, it also carries higher risk, as growth stocks are often more volatile. For younger investors with a longer investment horizon, this risk is acceptable, as they have more time to recover from potential losses. Growth investing represents a proactive approach to money management, with the potential for significant financial gains.
The Rise of Fractional Shares: Democratizing Investment Access
Fractional share investing is equally popular among Gen Z and Millennials at 48%, enabling investors to buy partial shares of expensive stocks. This trend reflects the increasing accessibility of the stock market, where investors can diversify their portfolios without needing substantial upfront capital. For Gen Z, in particular, fractional shares offer a way to invest in high-value companies like Amazon or Tesla, which may otherwise be out of reach. This democratization of investing aligns with a broader shift toward financial inclusion, empowering individuals to grow their wealth with smaller investments.
Short-Term Trading: A Growing Appetite for Quick Gains
Short-term trading, favored by 52% of both Gen Z and Millennials, highlights a desire for quick gains. This strategy, which involves buying and selling securities over a short period, appeals to younger investors who are more willing to take risks for potentially high rewards. However, short-term trading can be financially demanding, requiring significant time and attention to market trends. For those with a keen interest in finance and market dynamics, short-term trading can be a lucrative, albeit risky, strategy to maximize money.
Direct Indexing: Tailored Investment Portfolios
Direct indexing, chosen by 44% of Gen Z and 42% of Millennials, allows investors to personalize their portfolios by directly investing in the components of an index. This approach enables greater control over specific investments, allowing individuals to align their portfolios with personal financial goals or values. Although less popular among Gen X and Boomers, direct indexing represents a modern approach to money management, offering flexibility and customization that can appeal to a younger, tech-savvy demographic.
Socially Responsible Investing: Aligning Values with Financial Goals
Socially responsible investing (SRI) resonates particularly with Millennials (45%) and Gen Z (43%), reflecting a trend toward aligning financial decisions with personal values. SRI focuses on companies that prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, appealing to investors who wish to support sustainable and ethical businesses. For younger generations, investing is not just about financial returns; it’s about making a positive impact on the world. This values-driven approach to money reflects a broader societal shift toward conscious consumption and responsible investment.
Conclusion
Each generation brings unique perspectives and priorities to investing, influenced by economic conditions, technological advancements, and personal values. From the stability of buy-and-hold to the impact-driven goals of socially responsible investing, these strategies reflect the diverse ways people approach money management. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, understanding these generational preferences can help investors make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.