Loonie VS U.S. Dollar: A Financial Perspective
-
Jan, Tue, 2025
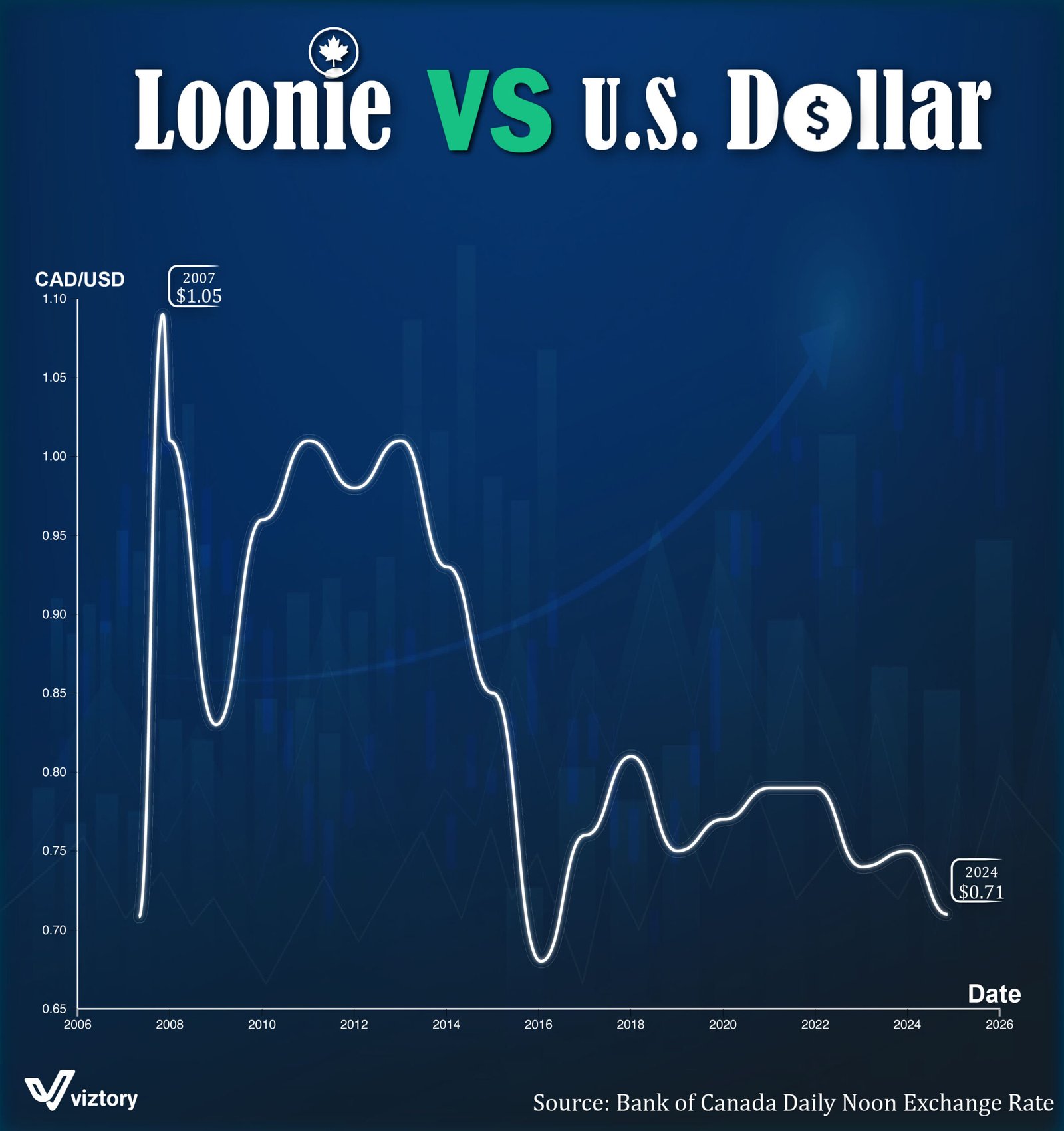
The relationship between the Canadian dollar, known as the “Loonie,” and the U.S. dollar has been a subject of economic analysis for decades. The graph illustrates the fluctuations in the exchange rate of the Canadian dollar against its American counterpart from 2006 to 2024. This data reveals significant economic shifts, global trends, and financial decisions that have impacted the value of these two currencies.
Key Milestones in the Exchange Rate
2007 Peak ($1.05 CAD/USD): The Canadian dollar reached parity and briefly surpassed the U.S. dollar in value. This peak was driven by booming commodity prices, particularly oil, which is a cornerstone of Canada’s export economy. The global demand for Canadian resources, coupled with a weaker U.S. dollar, fueled this historic moment.
Subsequent Decline (2008-2016): The financial crisis of 2008 marked the beginning of a downturn for the Loonie. As global demand slowed and oil prices dropped, the Canadian economy faced challenges, and the exchange rate fell below parity.
2016-2020 Stabilization: During this period, the exchange rate fluctuated but remained relatively stable, reflecting moderate economic recovery in Canada and consistent oil prices.
2024 Low ($0.71 CAD/USD): By 2024, the Loonie hit a significant low against the U.S. dollar. This decline is attributed to multiple factors, including a strong U.S. economy, rising interest rates in the U.S., and challenges within Canada’s resource-dependent economy, such as lower global demand for oil and natural gas.
Financial Implications of Exchange Rate Trends
For Canadian Exporters: A weaker Loonie benefits Canadian exporters by making their goods and services more affordable in the global market. However, it also highlights the country’s reliance on commodities.
For Canadian Consumers: On the flip side, a weaker currency increases the cost of imported goods, raising inflationary pressures and reducing purchasing power for Canadian households.
For Investors: Currency fluctuations offer opportunities and risks for investors. Those trading in forex markets or holding assets denominated in different currencies must navigate these changes carefully.
Broader Economic Context
The exchange rate between the Loonie and the U.S. dollar is influenced by:
- Oil Prices: As a major oil exporter, Canada’s economy is sensitive to global oil price trends.
- Interest Rates: Diverging monetary policies between the Bank of Canada and the U.S. Federal Reserve impact capital flows and exchange rates.
- Global Economic Trends: Geopolitical events, trade relationships, and economic growth in major economies all play a role in shaping currency values.
Looking Ahead
The future of the Loonie will depend on Canada’s ability to diversify its economy, reduce reliance on volatile commodity markets, and adapt to global economic shifts. While the current low exchange rate presents challenges, it also creates opportunities for growth in export-oriented industries.
In conclusion, the Loonie’s journey against the U.S. dollar reflects the complexities of global finance and the interconnectedness of economies. Understanding these trends is essential for businesses, consumers, and policymakers navigating the evolving financial landscape.