mpact of High Interest Rates on the Economy
-
Jul, Mon, 2024
Impact of High Interest Rates on the Economy
Introduction
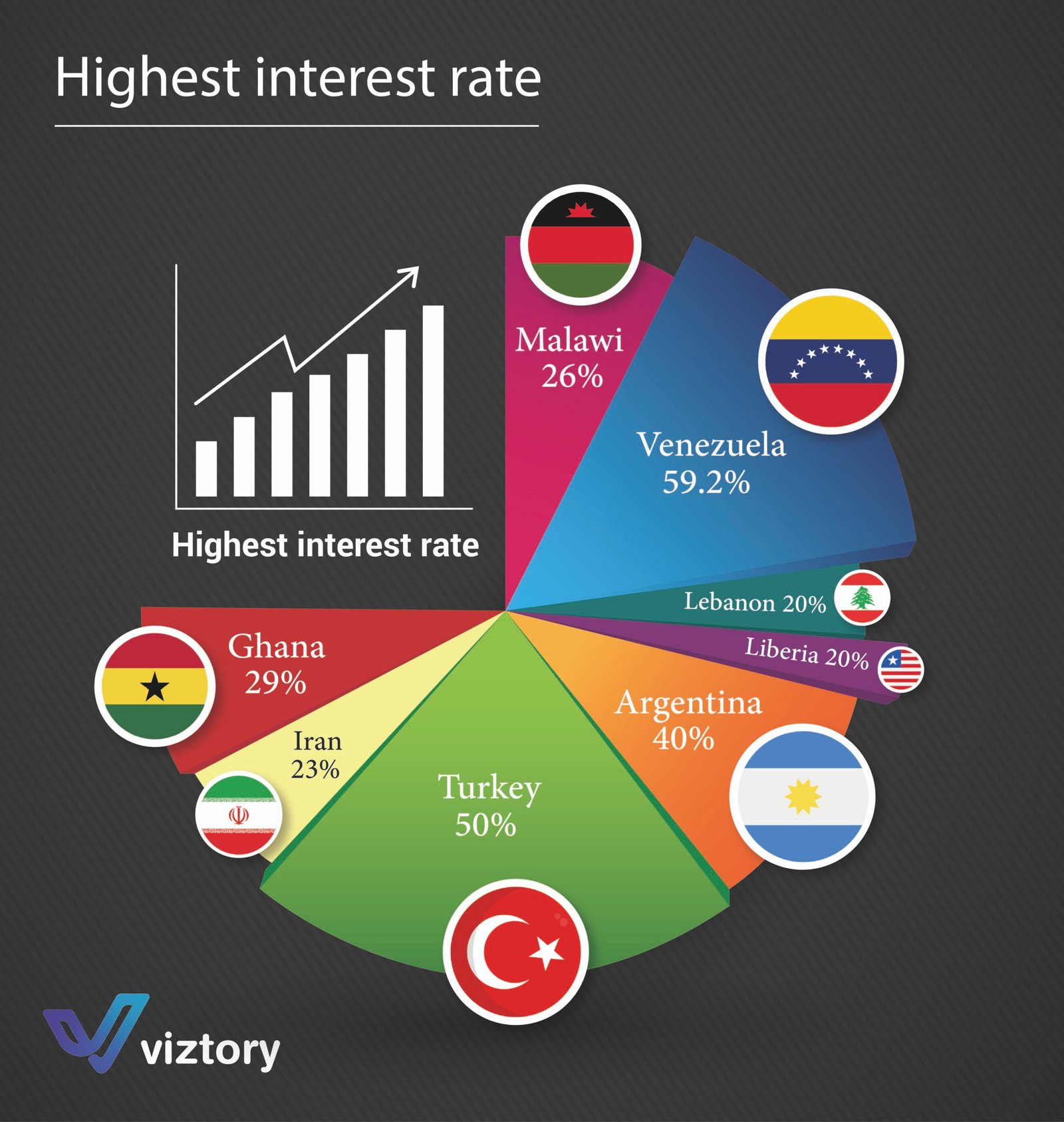
Interest rates play a crucial role in the global economy, affecting the financial decisions of individuals, businesses, and governments. The provided image shows a list of the highest interest rates worldwide, including the following countries: Venezuela, Turkey, Argentina, Ghana, Malawi, Iran, and Lebanon. These high rates reflect the unstable economic conditions in these countries. In this article, we will discuss the impact of these rates on the economy and how they can affect various economic aspects.
Countries and Interest Rates
-
Venezuela – 59.2%
- Venezuela is suffering from hyperinflation and ongoing economic turmoil. The high interest rate reflects efforts to combat inflation and attract investments, although it makes borrowing very expensive.
-
Turkey – 50%
- Turkey is another example of a country trying to combat inflation. The high-interest rate aims to stabilize the currency but negatively affects economic growth due to the high cost of borrowing.
-
Argentina – 40%
- Argentina also faces high inflation and a debt crisis. The high-interest rate reflects government efforts to control inflation and attract foreign capital.
-
Ghana – 29%
- In Ghana, the high-interest rate reflects efforts to maintain currency stability in the face of inflation and economic growth challenges.
-
Malawi – 26%
- Malawi follows similar monetary policies to deal with inflation and enhance currency stability, but this impacts borrowing costs and the ability to finance projects.
-
Iran – 23%
- Iran suffers from high inflation due to economic sanctions and financial policies. The high-interest rate aims to combat inflation and attract local investments.
-
Lebanon – 20%
- Lebanon is in the midst of a severe economic and political crisis. The high-interest rate reflects efforts to achieve financial stability amid currency collapse.
Impact of High Interest Rates on the Economy
1. Inflation: High-interest rates are a primary tool for combating inflation. When interest rates are high, borrowing becomes expensive, reducing spending and consumption, thus contributing to lowering inflation.
2. Economic Growth: High-interest rates hinder economic growth as they increase borrowing costs for companies and consumers, reducing investment and consumer spending.
3. Currency: High-interest rates help attract foreign investments, which can support the local currency. However, if rates are excessively high, they may lead to economic recession.
4. Unemployment: High-interest rates lead to economic slowdown, which can increase unemployment rates due to reduced investments and economic growth.
Conclusion
Interest rates are a crucial economic tool with wide-ranging impacts on the macroeconomy. As seen in the mentioned countries, high rates reflect attempts to combat inflation and attract investments, although they come with high economic costs such as slowed growth and increased unemployment. Understanding these dynamics helps in analyzing the global economic situation and predicting financial market movements and future economic policies.