Obesity and Healthcare: A Global Perspective
-
Aug, Thu, 2024
Obesity and Healthcare: A Global Perspective
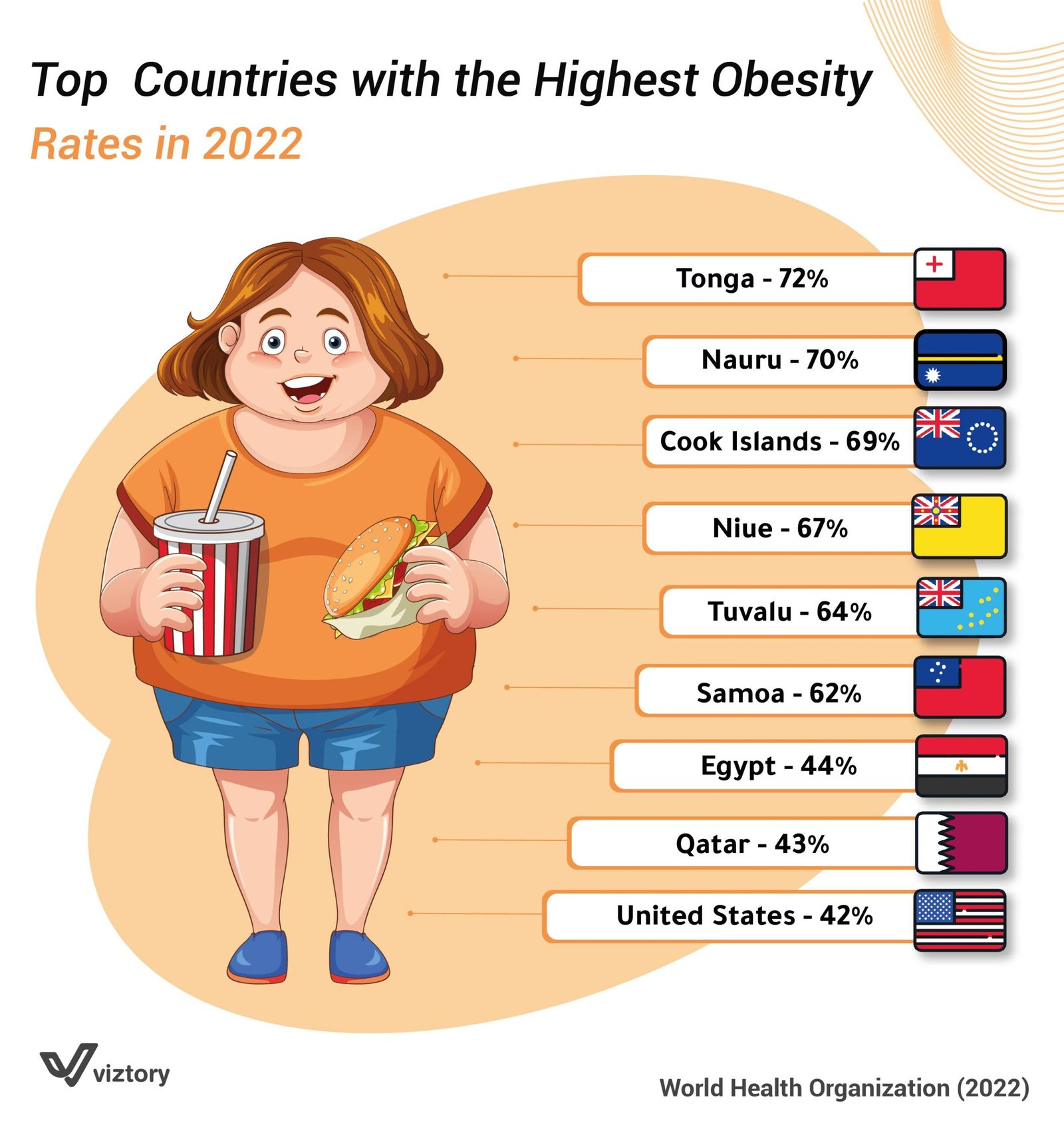
The image provided highlights the staggering obesity rates in various countries as of 2022, with some nations experiencing rates as high as 72%. Obesity, defined as an abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health, has become a global epidemic with significant implications for public health systems worldwide.
The Global Obesity Landscape
As depicted in the image, countries such as Tonga, Nauru, and the Cook Islands have some of the highest obesity rates globally, with 72%, 70%, and 69% respectively. These Pacific Island nations have consistently ranked high in obesity statistics due to a combination of factors including genetic predisposition, cultural shifts towards more sedentary lifestyles, and increased consumption of imported, processed foods that are high in sugar and fat.
In contrast, countries like Egypt, Qatar, and the United States, while having lower rates compared to the Pacific Islands, still show alarming obesity figures of 44%, 43%, and 42%, respectively. These statistics underline a growing public health crisis, as obesity is a major risk factor for a range of chronic diseases, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain cancers.
Implications for Healthcare Systems
The rising prevalence of obesity places a significant burden on healthcare systems across the globe. The management of obesity-related conditions requires substantial resources, both in terms of financial costs and medical personnel. In countries with high obesity rates, healthcare systems are often overwhelmed by the demand for services related to the treatment of obesity-related illnesses.
For instance, in the United States, healthcare spending on obesity-related issues is estimated to be in the hundreds of billions of dollars annually. This not only strains the financial resources of the healthcare system but also impacts the quality of care available to patients with other health conditions. Similarly, in countries with less robust healthcare systems, the rise in obesity-related illnesses can lead to inadequate care and increased mortality rates.
Addressing the Crisis
To mitigate the impact of obesity on healthcare systems, a multi-faceted approach is necessary. Public health initiatives aimed at promoting healthier diets and increased physical activity are crucial. Governments and healthcare providers must work together to implement policies that encourage healthy eating, such as taxes on sugary drinks and subsidies for fruits and vegetables. Education campaigns that raise awareness about the dangers of obesity and the benefits of a healthy lifestyle are also essential.
Moreover, healthcare systems need to be equipped to manage the growing number of patients with obesity-related conditions. This includes training healthcare professionals in obesity management and ensuring that there are adequate resources for the treatment of obesity and its associated diseases.
Conclusion
The image underscores the critical need for global attention to the obesity epidemic and its far-reaching consequences on healthcare systems. As obesity rates continue to rise, especially in specific regions, the strain on healthcare systems will only intensify. Addressing this issue requires comprehensive public health strategies and a concerted effort from all sectors of society. Only through such efforts can the tide of obesity be turned, ensuring healthier populations and more sustainable healthcare systems.
4o