Robots Leaders: Top Countries in Automation
-
Jan, Tue, 2025
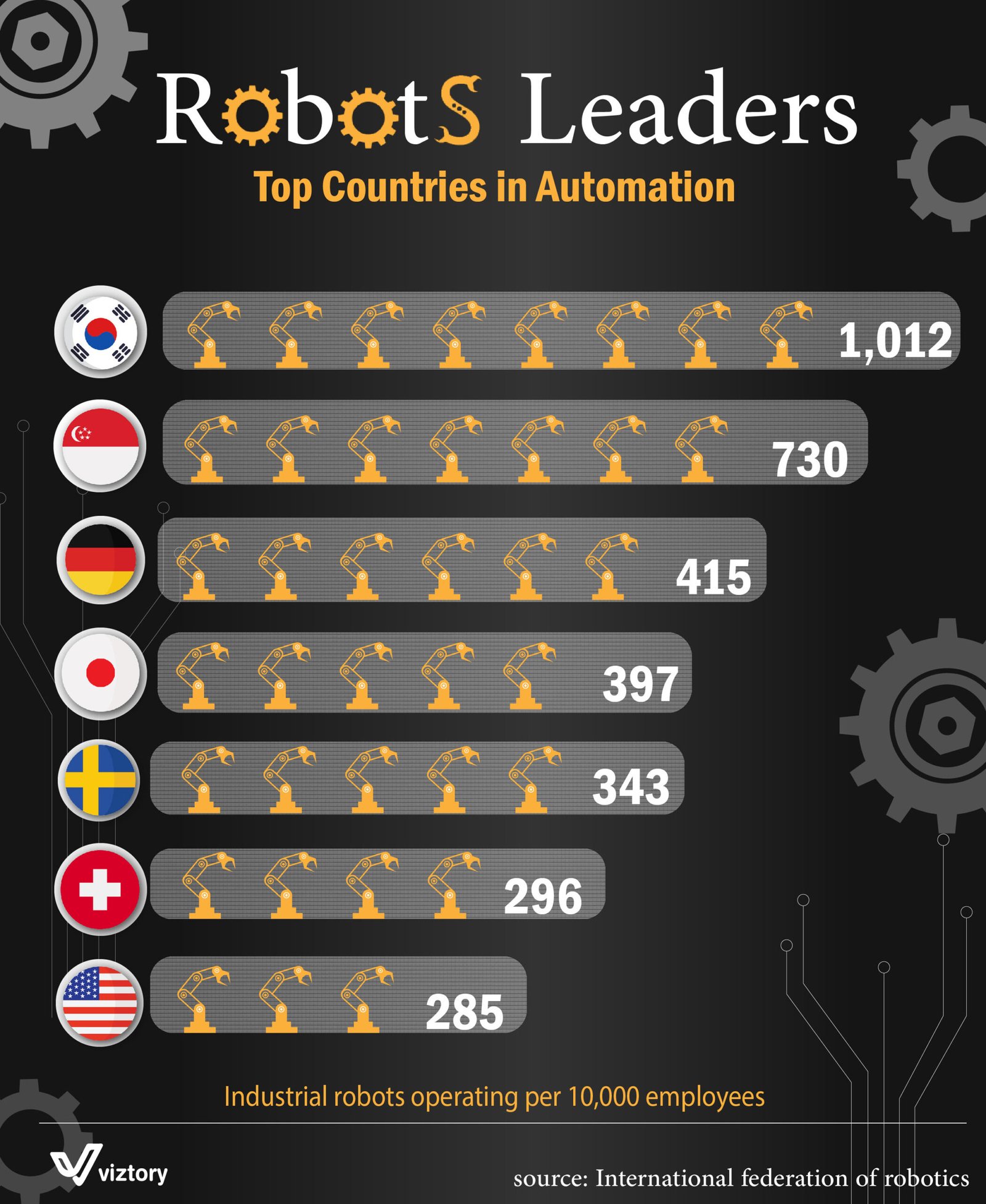
The rise of automation has reshaped global industries, with robotics playing a critical role in increasing efficiency and precision. The image highlights the top countries leading in industrial robotics, measured by the number of robots operating per 10,000 employees. At the forefront of this revolution, South Korea, Singapore, and Germany dominate the landscape, setting benchmarks for others to follow.
The Leaders in Industrial Robotics
South Korea (1,012 robots): Known for its advanced manufacturing sector, particularly in electronics and automotive, South Korea leads with an impressive ratio of robots per employee. Companies like Samsung and Hyundai heavily invest in robotics to maintain their competitive edge.
Singapore (730 robots): As a global hub for innovation, Singapore integrates robotics into its high-tech industries, ranging from precision engineering to pharmaceuticals.
Germany (415 robots): A powerhouse in engineering and manufacturing, Germany relies on robotics to maintain its global leadership in the automotive and industrial machinery sectors.
Japan (397 robots): A pioneer in robotics, Japan combines its expertise in technology and innovation to support industries like consumer electronics and automotive manufacturing.
Sweden (343 robots) and Switzerland (296 robots): These countries utilize robotics in precision engineering, pharmaceuticals, and specialized industries, showcasing their commitment to technological advancement.
United States (285 robots): With a focus on automotive, aerospace, and logistics, the U.S. steadily increases its reliance on automation to boost productivity and maintain global competitiveness.
The Role of Robotics in Industry
Robots have transformed industries by automating repetitive tasks, increasing production speeds, and reducing errors. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Robotics systems work tirelessly, minimizing downtime and maximizing output.
- Cost Reduction: Despite high initial investments, robots lower long-term costs by reducing waste and increasing precision.
- Safety Improvements: Dangerous tasks in industries like manufacturing and mining are now handled by robots, ensuring worker safety.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While automation drives industrial growth, it also presents challenges such as workforce displacement and the need for upskilling. Countries must invest in education and training programs to prepare their workforce for a highly automated future.
As technology evolves, robotics will continue to expand into new industries, such as healthcare, agriculture, and logistics. The countries leading this field are not only shaping their economies but also influencing the future of global industry.
In conclusion, the countries topping the robotics leaderboard have embraced innovation to remain competitive in a rapidly changing world. Their success serves as an example of how technology and automation can propel industrial and economic growth.