Satellite Internet: Bridging the Digital Divide with Advanced Technology
-
Aug, Thu, 2024
Satellite Internet: Bridging the Digital Divide with Advanced Technology
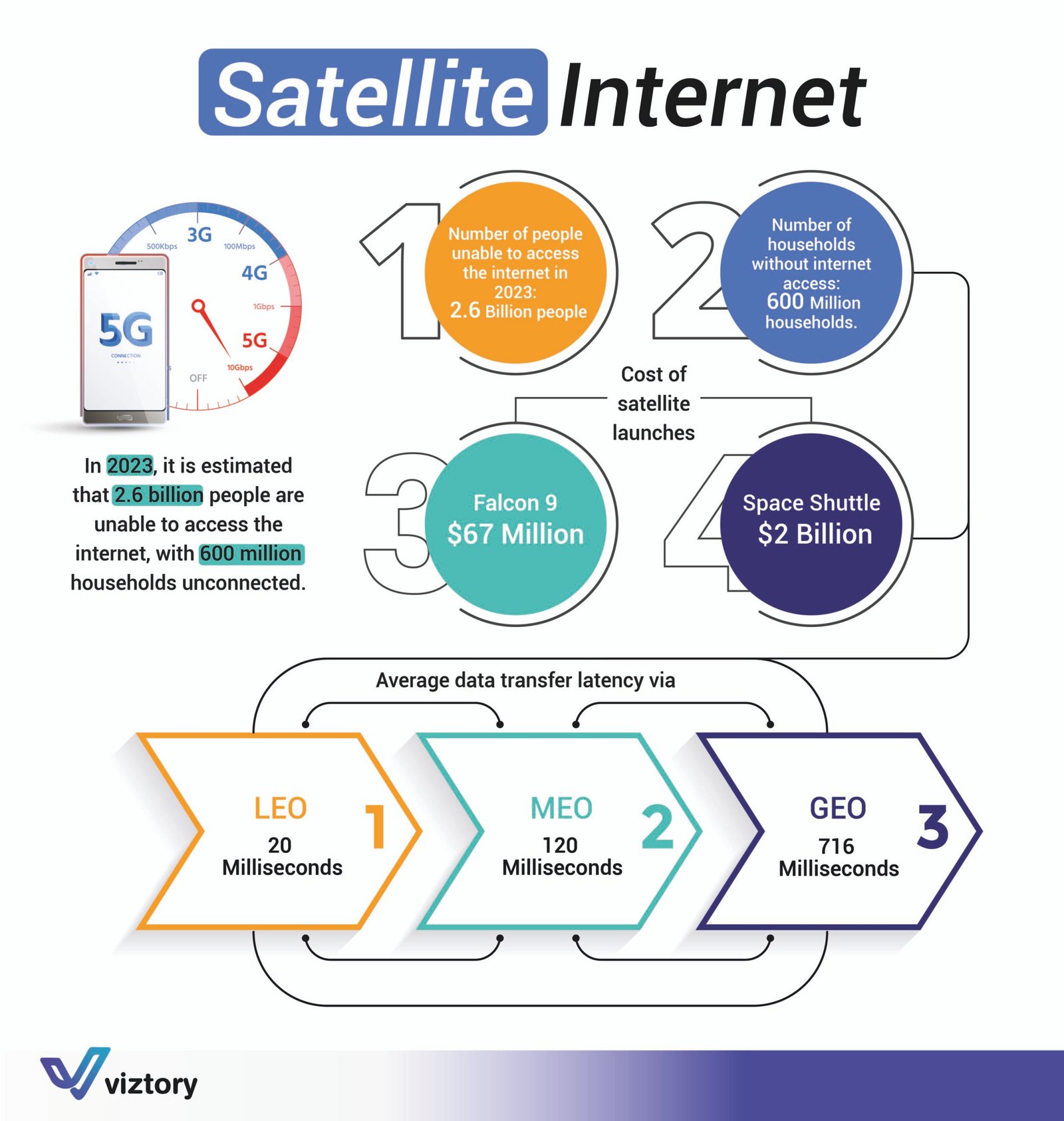
In the rapidly advancing technological landscape, access to the internet has become a crucial element for social and economic development. However, as of 2023, a staggering 2.6 billion people remain disconnected from the internet, with approximately 600 million households still lacking this essential utility. This digital divide highlights the urgent need for innovative solutions, such as satellite internet, to bring connectivity to underserved and remote regions.
Understanding Satellite Internet
Satellite internet is a form of broadband internet service that relies on satellites orbiting the Earth to provide internet access. Unlike traditional wired connections, satellite internet can reach areas where laying cables is either too expensive or physically impossible. This technology holds the promise of connecting even the most isolated communities, bridging the gap between the connected and the unconnected.
The Cost of Connectivity
Launching satellites into space is no small feat, both in terms of technology and cost. The infographic reveals that the cost of launching a satellite can range significantly depending on the vehicle used. For instance, launching a satellite with a Falcon 9 rocket costs about $67 million, whereas utilizing the Space Shuttle, a now-retired vehicle, could cost up to $2 billion. The high costs associated with these launches are one of the significant barriers to expanding satellite internet coverage globally.
Latency Considerations in Satellite Internet
Latency, or the time it takes for data to travel from the user’s device to the satellite and back, is a crucial factor in the performance of satellite internet. The infographic highlights the differences in latency between Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), and Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) satellites.
- LEO Satellites: These are closest to the Earth, with an average latency of 20 milliseconds. LEO satellites offer faster data transfer speeds, making them ideal for applications requiring real-time communication, such as video conferencing and online gaming.
- MEO Satellites: Positioned higher than LEO satellites, MEO satellites have a latency of around 120 milliseconds. While slower than LEO satellites, they still provide a good balance between coverage area and speed.
- GEO Satellites: Located much further from Earth, GEO satellites have a latency of about 716 milliseconds. These satellites cover a larger area and are commonly used for broadcast services and areas where other types of satellite internet are not feasible.
The Role of 5G in Satellite Internet
The integration of 5G technology with satellite internet promises to enhance connectivity by providing faster speeds and lower latency. The infographic illustrates how 5G is poised to revolutionize the way we access the internet, especially in remote regions where traditional 4G or broadband connections are unavailable.
The Future of Global Connectivity
The digital divide remains a significant challenge, but advancements in satellite internet technology, combined with the rollout of 5G, offer a viable path to universal internet access. As more satellites are launched and costs potentially decrease, the goal of connecting the 2.6 billion people currently without internet access becomes more attainable.
Through continued investment and innovation in satellite technology, we can hope to see a future where everyone, regardless of location, has access to the vast resources and opportunities the internet provides. The world is on the cusp of a new era of global connectivity, one where the internet is not a luxury, but a fundamental right for all.