Silver Supply Sources: Economic Importance and the Role of Money
-
Sep, Sat, 2024
Silver Supply Sources: Economic Importance and the Role of Money
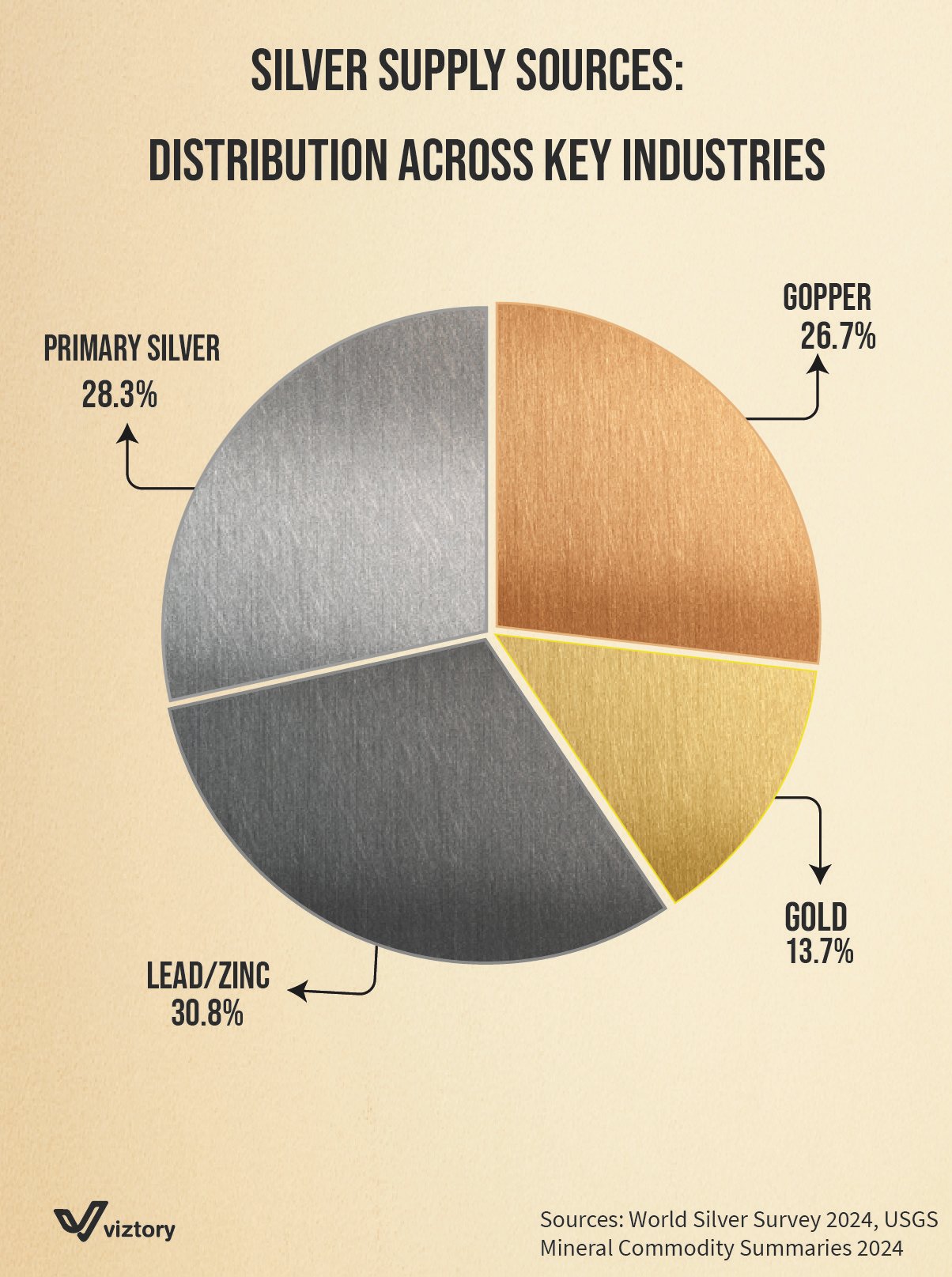
The supply of silver plays a critical role in various industries, influencing global markets and financial systems. The visualizations demonstrate the distribution of silver sources across key sectors, including lead/zinc (30.8%), primary silver (28.3%), copper (26.7%), and gold (13.7%). Each of these sectors contributes to the availability and pricing of silver, which is not only a valuable industrial metal but also an important component in the monetary systems of history and today.
Silver has long been used as a form of currency and remains a store of value, much like gold. Its role in the world of money is tied to its historical use in coins and, more recently, as an investment asset. As silver is mined alongside other metals, such as lead and copper, fluctuations in these industries can directly affect the silver market, influencing its supply and price. Investors and financial institutions closely monitor these dynamics to gauge the availability of silver, its potential scarcity, and its effect on economic stability.
Furthermore, silver’s role in money extends to its use in bullion, where it is traded as a form of wealth preservation. Many investors see silver as a hedge against inflation and economic downturns, particularly during periods of financial instability. The visualizations underscore how primary silver mining and its recovery from other metals contribute to the overall silver market, which in turn affects monetary policies and investment decisions globally.
In conclusion, the distribution of silver supply sources is closely intertwined with the concept of money. As both an industrial metal and a financial asset, silver’s availability and pricing have profound implications for economies and monetary systems worldwide, reinforcing its long-standing status as a precious metal and a reliable store of value.