The Impact of Data Centers’ Power Consumption on the Global Economy
-
Aug, Mon, 2024
The Impact of Data Centers’ Power Consumption on the Global Economy
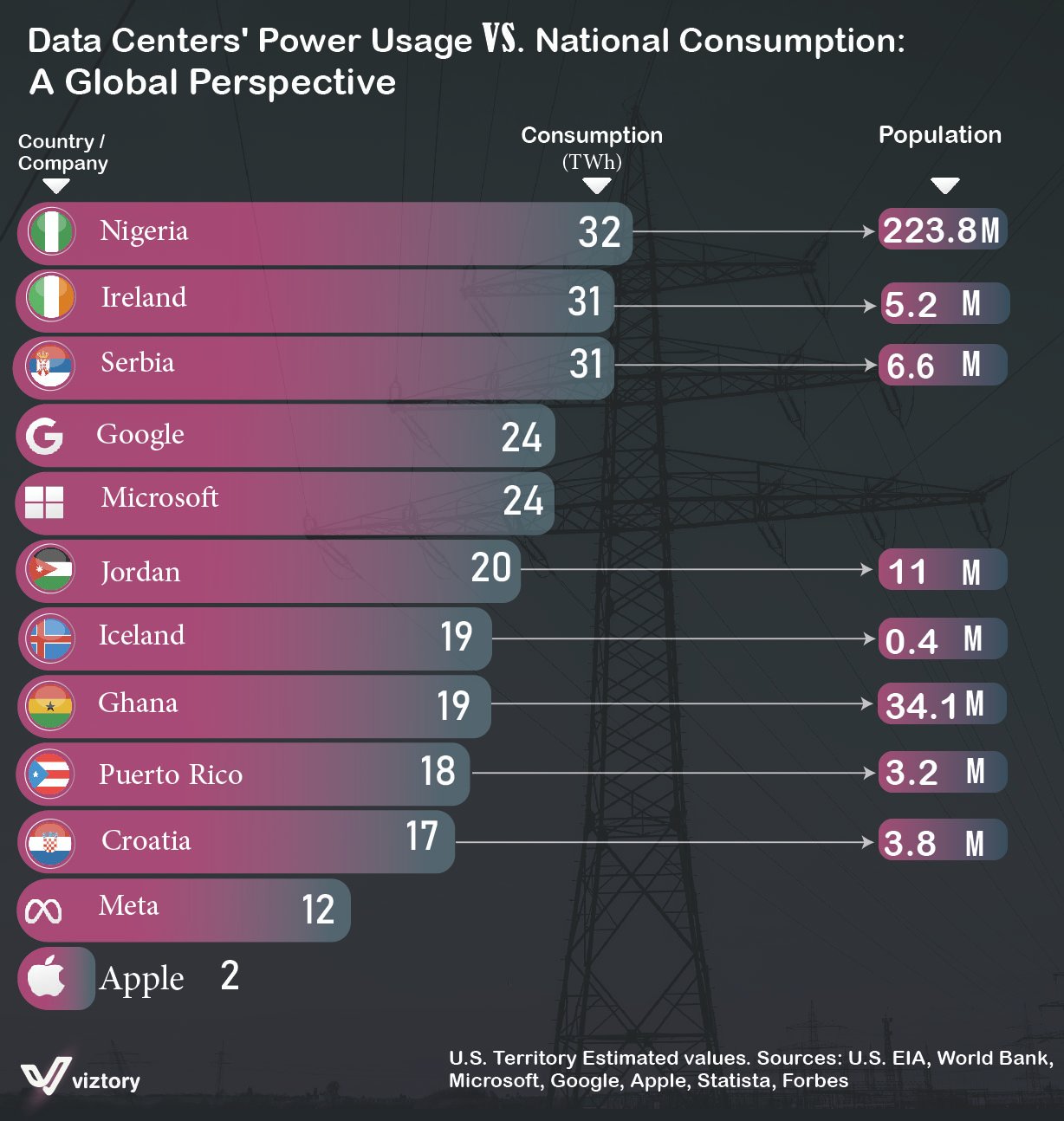
In recent decades, the world has witnessed a radical shift towards a digital economy, where data has become the driving force behind many economic activities. As reliance on data increases, the importance of data centers, which serve as the backbone for storing and processing this data, has also grown. The image provided compares the power consumption of major tech companies’ data centers with that of some countries from a global perspective, highlighting the significance of these centers and their economic impact.
Investment in Energy: A Challenge and an Evolution
The image shows that the power consumption of data centers for companies like Google and Microsoft exceeds that of some nations. For instance, both Google and Microsoft consume 24 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity annually, a figure roughly equivalent to the entire consumption of countries like Jordan and Iceland. These numbers highlight the massive investment required to keep these centers operational, as they demand vast amounts of energy to maintain continuous operations 24/7.
This high energy consumption has multiple economic implications. First, providing this energy necessitates substantial investments in energy infrastructure, whether through traditional or renewable sources. Second, the large demand for energy can lead to higher electricity costs, which in turn affects the operating costs of data centers and, subsequently, company profits.
Small Economies vs. Tech Giants
Looking at the image, it becomes evident that the energy consumption of major tech companies is comparable to or even exceeds that of some small countries. For example, Microsoft’s energy consumption (24 TWh) surpasses that of Croatia (17 TWh), while Meta (formerly Facebook) consumes about 12 TWh, which is close to the energy consumption of Iceland (19 TWh), a country with a population of only 400,000.
Economic Impacts and Challenges
This disparity in energy consumption highlights the economic gap between large companies and small countries. While these companies possess vast financial resources that allow them to invest in renewable energy solutions and more energy-efficient technologies, small nations may find themselves facing significant challenges in providing energy for their citizens and achieving economic growth.
Moreover, this disparity raises questions about economic and environmental sustainability, especially given the growing global pressures to reduce carbon emissions and achieve sustainable development goals. Although companies like Google and Apple commit to using 100% renewable energy, their significant energy consumption still poses a considerable challenge.
Conclusion
The increasing power consumption of data centers reflects the tremendous growth of the digital economy but also presents significant challenges related to economic and environmental sustainability. Major companies need to continue innovating in energy efficiency and investing in renewable energy, while smaller countries must find ways to adapt to these global changes. Ultimately, achieving a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability is a shared goal that requires global cooperation and concerted efforts.