The Rising Cost of Insulin and Its Impact on Healthcare
-
Sep, Sun, 2024
The Rising Cost of Insulin and Its Impact on Healthcare
Over the past few decades, the cost of insulin, a life-saving medication for millions of people with diabetes, has been on a steep incline. This rise in price has had significant implications for healthcare systems globally, affecting accessibility and affordability for patients who rely on this essential drug.
Insulin Pricing Trends
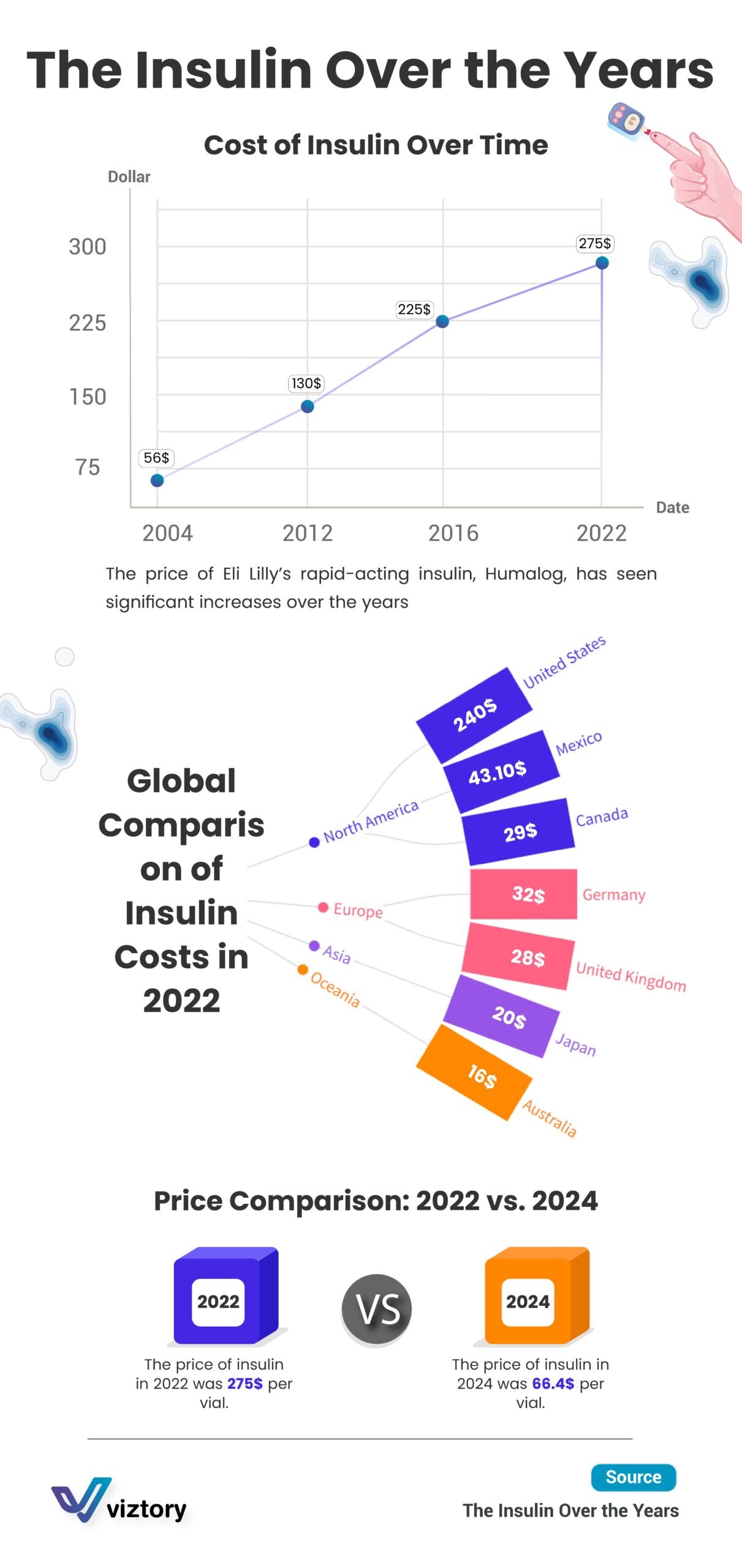
The image provided highlights the stark increase in the price of Eli Lilly’s rapid-acting insulin, Humalog, over time. In 2004, a vial of insulin was priced at $56, but by 2022, this price had soared to $275. This near fivefold increase over 18 years has been a major cause of concern for patients, healthcare providers, and policymakers alike. The trend depicted underscores the growing financial burden on individuals who need insulin daily to manage their condition.
Global Comparison of Insulin Costs
The image also provides a global comparison of insulin costs in 2022, showing significant price disparities across different regions. For instance, the cost of insulin in the United States was a staggering $240 per vial, far higher than in other countries such as Canada ($29), Germany ($32), and Australia ($16). These disparities highlight the varying impacts of healthcare policies, market regulations, and pharmaceutical pricing strategies on the cost of essential medications.
Price Adjustments in 2024
Interestingly, the image notes a significant decrease in insulin prices by 2024, where the cost in the U.S. drops to $66.4 per vial. This reduction could be the result of various factors such as governmental interventions, pricing reforms, and increased market competition, all aimed at making this critical drug more affordable. Such a decrease represents a positive shift towards more equitable healthcare, ensuring that more patients can access the insulin they need without facing financial hardship.
Implications for Healthcare
The escalating cost of insulin has profound implications for healthcare systems. High drug prices can lead to increased insurance premiums, higher out-of-pocket costs for patients, and significant financial strain on public health programs like Medicare and Medicaid. For patients, especially those uninsured or underinsured, the high cost of insulin can lead to rationing, skipping doses, or even foregoing the medication altogether, which can have severe health consequences, including life-threatening complications.
On a broader scale, the high cost of insulin and other essential medications raises questions about the sustainability of current healthcare models. It also prompts a discussion on the role of pharmaceutical companies, government regulations, and healthcare providers in ensuring that life-saving drugs remain affordable and accessible to all who need them.
Conclusion
The image encapsulates a critical issue in healthcare: the affordability of essential medications like insulin. While the projected decrease in insulin prices by 2024 offers hope, the historical trend of rising costs serves as a reminder of the challenges that still lie ahead. Ensuring access to affordable healthcare, including necessary medications, remains a crucial goal for policymakers, healthcare providers, and patient advocates worldwide. The healthcare community must continue to work together to address these disparities and create a system that prioritizes patient well-being over profits.