Who Does the EU Trade With?
-
Oct, Fri, 2024
Who Does the EU Trade With? Marketing Implications in Global Trade
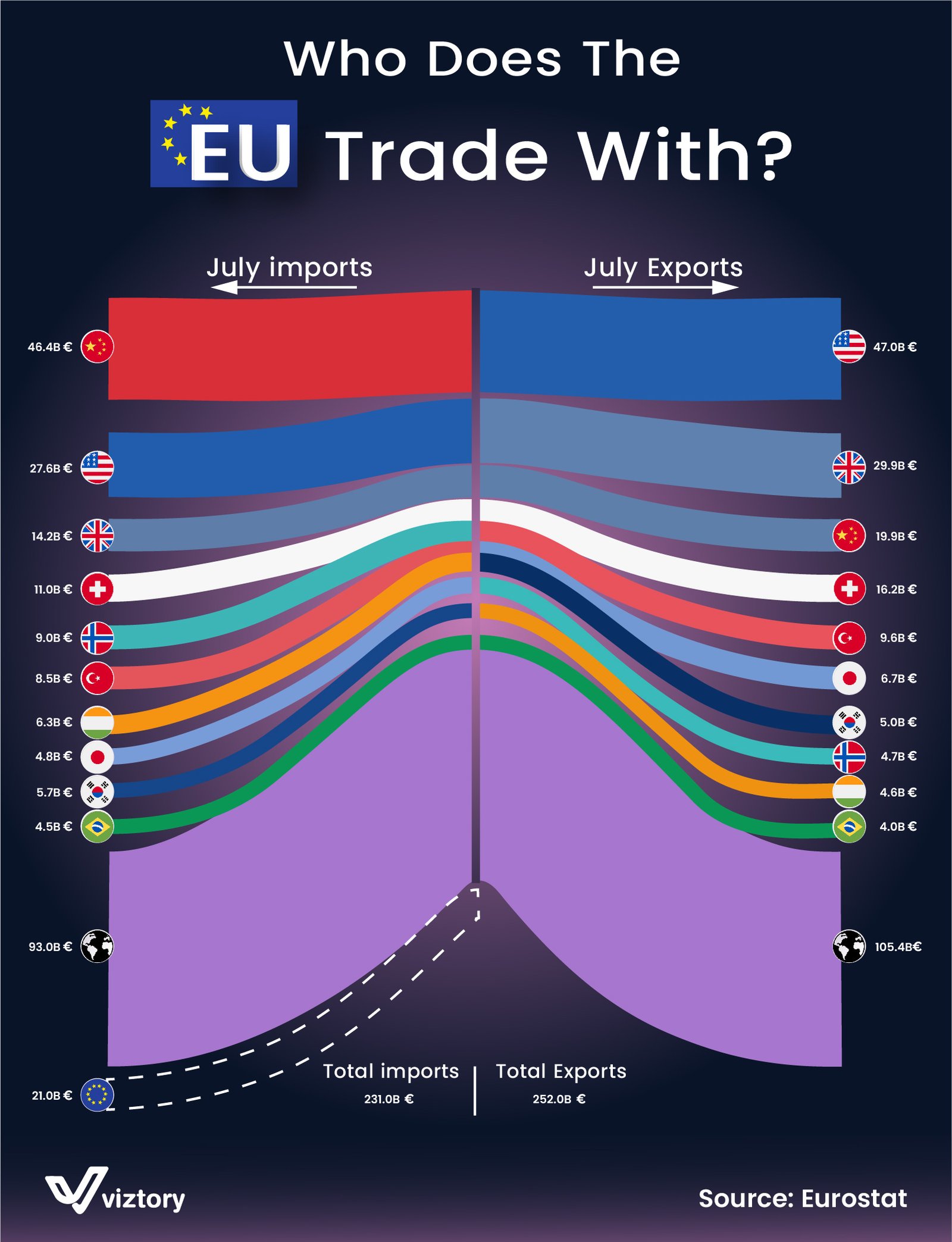
The visualization showcases the European Union’s (EU) trade relationships, highlighting both imports and exports with key trading partners in July. The EU imports €231 billion worth of goods, while its exports amount to €252 billion. The United States (€47.08 billion in exports) and China (€46.4 billion in imports) dominate the EU’s trade relationships, followed by other major partners such as the UK, Switzerland, and Turkey. Understanding these trade dynamics is essential for businesses seeking to enter or expand in the global market. This article explores how international trade affects marketing strategies, with a focus on the EU’s largest trade partners.
Global Trade and Its Impact on Marketing
Global trade significantly influences marketing strategies by shaping how companies approach market entry, pricing, supply chains, and brand positioning. As businesses look to expand internationally, they must tailor their marketing efforts to the specific economic, regulatory, and cultural contexts of each market.
For the EU, its diverse set of trading partners presents both opportunities and challenges for marketers. Each country or region involved in trade with the EU has distinct consumer preferences, regulatory environments, and competitive landscapes, all of which influence how companies position their products and services.
The United States: A Key Export Market for the EU
The United States is the EU’s largest export destination, with €47.08 billion worth of goods exported in July alone. The strong trade relationship between the EU and the U.S. is underpinned by shared interests in sectors such as technology, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and luxury goods. For marketers, the U.S. represents a lucrative market, but it also comes with intense competition.
To succeed in the U.S., EU companies need to adopt marketing strategies that emphasize innovation, quality, and brand differentiation. This is particularly important in sectors like technology and automotive, where American consumers are accustomed to high standards and constant technological advancements. Digital marketing and localized content are essential for reaching U.S. consumers, given the high internet penetration and the importance of platforms like Google, Facebook, and Amazon in shaping purchasing decisions.
Additionally, the U.S. market often requires a more aggressive advertising approach, with a focus on brand building and visibility. This is in contrast to many European markets, where subtlety and long-term relationship building may be more effective.
China: The EU’s Largest Import Source
China leads the EU’s imports, with €46.4 billion in goods flowing into the EU in July. China’s role as the world’s manufacturing hub makes it a vital source of goods for the EU, particularly in sectors such as electronics, machinery, and textiles. For EU-based companies looking to sell in China, however, marketing strategies must navigate complex regulatory requirements and cultural differences.
Chinese consumers place a high value on trust, brand reputation, and quality. As the middle class continues to grow, there is increasing demand for European luxury goods, high-end automotive products, and advanced technology. Brands that successfully market their products in China often emphasize their heritage, craftsmanship, and superior quality. Leveraging platforms like WeChat, Alibaba, and Douyin (TikTok) is crucial for engaging with Chinese consumers, as these digital ecosystems dominate China’s retail and social media landscapes.
The UK: A Historical Trade Partner
Despite Brexit, the UK remains a significant trading partner for the EU, with €14.2 billion in imports and €29.9 billion in exports. The UK’s proximity to Europe and long history of trade make it an attractive market for EU businesses, but the regulatory landscape has changed post-Brexit, affecting marketing strategies.
Marketers must now account for different regulatory standards, customs procedures, and tariffs when trading with the UK. However, the shared language and cultural familiarity between the UK and many EU countries make the UK a relatively easier market to navigate compared to others. EU companies targeting the UK market need to focus on maintaining strong brand loyalty while adapting to changes in trade regulations and consumer behavior.
Marketing to Switzerland and Turkey: Regional Differences
Switzerland (€11 billion in imports and €16.28 billion in exports) and Turkey (€8.5 billion in imports and €9.6 billion in exports) represent important trading partners for the EU, each with unique market characteristics. Switzerland is known for its high-income consumers and stable economy, making it an ideal market for luxury goods, pharmaceuticals, and high-tech products.
In contrast, Turkey’s large, young population and rapidly growing economy make it a key market for affordable consumer goods, automotive products, and industrial machinery. Marketing strategies in Turkey must account for regional differences within the country, as well as fluctuating economic conditions and evolving consumer preferences. Digital marketing is on the rise in Turkey, and companies can tap into the growing e-commerce sector by leveraging social media and online marketplaces.
Global Trade Marketing: Tailoring Strategies to Diverse Markets
Effective marketing in the context of global trade requires a deep understanding of each market’s cultural, regulatory, and economic environment. As the visualization shows, the EU’s trade relationships span the globe, from the U.S. and China to smaller but significant partners like South Korea, Japan, and Brazil.
Each of these markets requires a tailored approach:
- In Japan and South Korea, marketing strategies should focus on high-tech innovations and quality, as consumers in these countries are highly discerning and value technological advancements.
- In Brazil, EU companies need to be mindful of economic volatility and local competition, emphasizing affordability and local partnerships to succeed in this dynamic market.
Moreover, marketing strategies should align with global trade agreements, tariffs, and logistical challenges. EU companies looking to enter or expand in these markets must also consider the implications of trade barriers, currency fluctuations, and supply chain management on their marketing efforts.
Digital Marketing’s Role in Global Trade
Digital marketing is increasingly becoming the linchpin of global trade marketing strategies. Platforms like Amazon, Alibaba, and Mercado Libre are essential for reaching consumers in key markets like the U.S., China, and Latin America. Companies can use data analytics to better understand consumer preferences and optimize their marketing campaigns for different regions.
Social media marketing also plays a critical role in connecting with international audiences. For example, Instagram and Facebook dominate in the U.S. and Europe, while WeChat, Douyin, and Alibaba are crucial for engaging Chinese consumers. By leveraging these platforms, companies can create targeted, culturally relevant content that resonates with local audiences.
Conclusion: Strategic Marketing in Global Trade
The EU’s trade relationships with global partners, as depicted in the visualization, demonstrate the importance of understanding and navigating diverse markets. Marketing strategies must be adapted to each country’s unique characteristics, whether it’s the U.S.’s demand for cutting-edge technology, China’s focus on quality and trust, or Turkey’s growing e-commerce market.
By tailoring marketing efforts to each region, understanding local consumer behavior, and leveraging digital platforms, EU companies can strengthen their positions in international markets. As global trade continues to evolve, the integration of strategic marketing will be essential for businesses to thrive in an increasingly interconnected world.