Women in Leadership: Global Rise from 1960 to 2024
-
Sep, Thu, 2024
Women in Leadership: Global Rise from 1960 to 2024
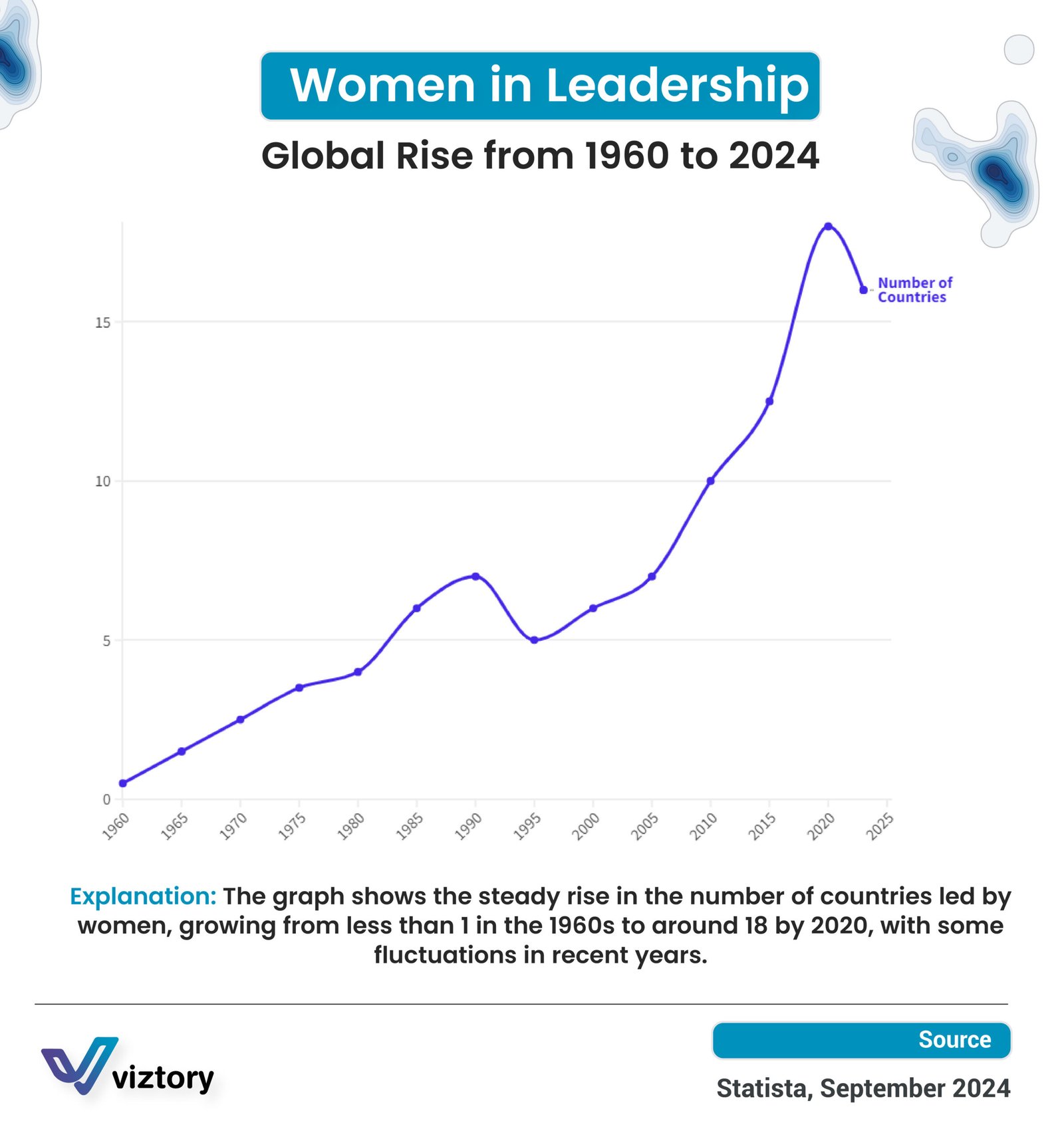
The graph illustrates the significant rise in the number of countries led by women from 1960 to 2024. Beginning with fewer than one country in the 1960s, the number has steadily increased, reaching around 18 by 2020, with notable fluctuations in recent years. This upward trend reflects the growing influence and presence of women in leadership roles across the globe, a development that intersects with broader conversations about gender equality, political empowerment, and societal progress.
The Global Trend Toward Female Leadership
The rise in female leadership marks a crucial shift in the global political landscape. The 1960s saw few women in such positions, but over the decades, this number has risen as barriers to gender equality have slowly eroded. Countries around the world have embraced female leaders, reflecting changes in societal attitudes, education, and political reforms that promote inclusivity and gender equity.
This trend is driven by global movements advocating for women’s rights and empowerment, such as the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which emphasize the importance of women’s participation in leadership and decision-making processes. The surge in female leaders across the globe highlights the successful integration of women in spaces previously dominated by men, creating a more balanced and representative governance system.
Women in Leadership in the Middle East
The Middle East, historically seen as a region with deep-rooted patriarchal structures, has also witnessed notable shifts in the realm of women’s leadership, though progress varies widely from country to country. In recent years, there has been a gradual rise in the presence of women in politics, government, and business in the region, reflecting changing attitudes toward gender roles and empowerment.
For example, countries like the United Arab Emirates (UAE) have introduced groundbreaking initiatives to promote gender balance in leadership, such as appointing female ministers and pushing for greater female representation in both public and private sectors. Saudi Arabia, once among the most restrictive nations for women, has recently allowed women to participate in public life more openly, including changes to laws that enable women to work in diverse industries, vote, and run for office.
While the Middle East has yet to see a widespread embrace of women leaders at the highest level of government, there are growing signs of progress, with women increasingly taking on leadership roles in various sectors. Education reforms, coupled with national policies aiming for gender equality, are paving the way for the next generation of female leaders in the region.
Challenges and Opportunities
The rise of women in leadership globally and in the Middle East does not come without challenges. Women in leadership often face gender biases, societal expectations, and structural barriers that men do not encounter. In many parts of the Middle East, traditional cultural norms still limit the scope of women’s participation in political and economic spheres.
However, with ongoing reforms, advocacy for gender parity, and the increasing visibility of successful female leaders, there is a sense of optimism that the future holds more opportunities for women to step into leadership roles across the Middle East. By integrating women into decision-making processes, countries can benefit from diverse perspectives, fostering innovation and more inclusive governance.
Conclusion
The steady rise of women in leadership from 1960 to 2024 is a reflection of global efforts to bridge the gender gap in political and executive roles. The Middle East, while still facing certain cultural and societal challenges, is part of this global trend as more women emerge as leaders in politics, business, and public life. This shift towards more inclusive leadership marks an essential step toward achieving gender equality and building stronger, more representative governance systems across the world.